Page 124 - The Indian Optician Digital Edition March-April 2024
P. 124
is also base down and out. setting is inclined at exactly the correct angle to
the cylinder axis direction.
Point (b) lies 3mm inwards from the
geometrical centre of the cylinder +4.00 DC PRISMATIC EFFECT OF
x 30, hence, GR = 3 and PR = c = 3 sin 30 = SPHERO-CYLINDERS
120
1.5mm or 0.15 cm. Using P = c F = 0.15 x 4
120
120
= 0.6Δ base down at 120. A sphero-cylindrical prescription may be
looked upon in either of two ways. We could
The oblique prismatic effects can be look upon a sph-cyl. as a spherical lens to which
resolved into vertical and horizontal has been added a plano-cylinder, or, we may
components as required. consider it to be made up from two separate
DECENTRATION OF CYLINDRICAL plano-cylinders placed together with their
LENSES axes at right angles to one another. It should
be apparent that we are only interested in the
A cylindrical lens may be decentred to principal powers of the lens and not in its form,
produce a prescribed prismatic effect only when so the remarks here apply equally to toric lenses.
the prism base direction coincides with the
power meridian. Hence, a cylinder whose axis Consider the lens +2.00 DS/+2.00 DC x 90
lies in the vertical meridian can only produce for which it is required to find the prismatic
horizontal prismatic effect and a cylinder whose effect introduced by the lens when the eye
axis lies in the horizontal meridian can only views through a point 5mm above and 5mm
produce vertical prismatic effect. Thus, the inwards from the optical centre. Treating the
prescription, +2.00 DC x 90 & 1Δ base in, may lens as a sphere and a plano-cylinder we have
be fulfilled by decentring the cylinder 5mm the following:
inwards, the decentration being found just as for
spherical lenses. When the prism base direction c = 0.5cm c = 0.5cm
V
H
does not coincide with the power meridian F = +2.00 F = +2.00
the prism must be obtained by working the sph cyl
refracting faces at the correct angle to one The prism due to the sphere = c F sph = 1Δ base
V
another, i.e., by working the prism onto the lens. down and c F sph = 1Δ base out.
H
The necessary thickness difference along the The prism due to the cylinder = c F = 0 and
base setting is found by the usual methods. The V cyl
workshop must of course ensure that the base c F = 1Δ base out.
cyl
H
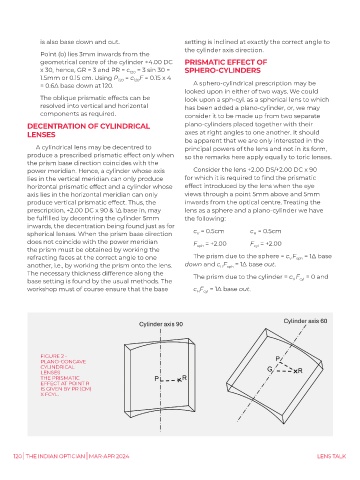
FIGURE 2 -
PLANO-CONCAVE
CYLINDRICAL
LENSES
THE PRISMATIC
EFFECT AT POINT R
IS GIVEN BY PR (CM)
X FCYL.
120 | THE INDIAN OPTICIAN | MAR-APR 2024 LENS TALK