Page 132 - The Indian Optician Digital Edition March-April 2024
P. 132
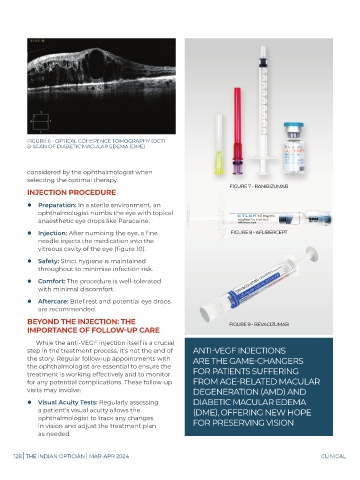
FIGURE 6 - OPTICAL COHERENCE TOMOGRAPHY (OCT)
B-SCAN OF DIABETIC MACULAR EDEMA (DME)
considered by the ophthalmologist when
selecting the optimal therapy.
INJECTION PROCEDURE
Preparation: In a sterile environment, an
ophthalmologist numbs the eye with topical
anaesthetic eye drops like Paracaine.
Injection: After numbing the eye, a fine
needle injects the medication into the
vitreous cavity of the eye (figure 10).
Safety: Strict hygiene is maintained
throughout to minimise infection risk.
Comfort: The procedure is well-tolerated
with minimal discomfort.
Aftercare: Brief rest and potential eye drops
are recommended.
BEYOND THE INJECTION: THE
IMPORTANCE OF FOLLOW-UP CARE
While the anti-VEGF injection itself is a crucial
step in the treatment process, it's not the end of ANTI-VEGF INJECTIONS
the story. Regular follow-up appointments with ARE THE GAME-CHANGERS
the ophthalmologist are essential to ensure the
treatment is working effectively and to monitor FOR PATIENTS SUFFERING
for any potential complications. These follow-up FROM AGE-RELATED MACULAR
visits may involve: DEGENERATION (AMD) AND
Visual Acuity Tests: Regularly assessing DIABETIC MACULAR EDEMA
a patient's visual acuity allows the (DME), OFFERING NEW HOPE
ophthalmologist to track any changes
in vision and adjust the treatment plan FOR PRESERVING VISION
as needed.
128 | THE INDIAN OPTICIAN | MAR-APR 2024 CLINICAL