
Dr Prof Mo Jalie
DSc, SMSA, FBDO (Hons), SLD, Hon FCGI Hon FCOptom, MCMI, is a Visiting Professor of Optometry at the University of Ulster in Coleraine, and at the post-graduate facility at Varilux University. He served for nine years as Head of Department of Applied Optics at City & Islington College, where he taught optics, ophthalmic lenses and dispensing. He is a recognised international authority on spectacle lens design and has written several books including Principles of Ophthalmic Lenses. His most recent book, Ophthalmic Lenses & Dispensing was translated into Russian. He has authored over 200 papers on ophthalmic, contact and intra- ocular lenses, and on dispensing; and is a consultant editor to The Optician (UK) and technical editor to The Indian Optician journal. He holds patents for aspheric spectacle and intra-ocular lenses. Jalie is a past-chairman of the Academic Committee of the Association of British Dispensing Opticians, and was the first Chairman of the Faculty of Dispensing Opticians. He is the ABDO representative on the BSI committees on ophthalmic lenses and spectacle frames and a past member of the Education Committee of the General Optical Council. In 1998 Jalie was thrice honoured: he was made Honorary Fellow of the British College of Optometrists, a Life Fellow of the Association of British Dispensing Opticians, and in December of that year he was granted the Max Wiseman Memorial Research Medal.
A sphero-cylindrical prescription may be looked upon in either of two ways. One could look upon a sph-cyl. as a spherical lens to which has been added a plano- cylinder, or, we may consider it to be made up from two separate plano-cylinders placed together with their axes at right angles to one another. It should be apparent that we are only interested in the principal powers of the lens and not in its form, so the remarks here apply equally to toric lenses.
Find the prismatic effects at a point 8mm above and 3mm inwards from the optical centre of the lens R -6.00 DS/+2.00 DC x 40.
The graphical construction is shown in Figure 1. The powers of the lens are -6.00 D along 40 and -4.00 D along 130 and these have been marked upon the principal meridians.
By measurement:
RP = c40 = 0.75cm and RQ = c130 = 0.42cm.
So, P40 = c40 x F40 = 0.75 x 6 = 4.5Δ base up @ 40,
(Since the power along 40, F40, is negative, point P represents the position of the prism apex).
P130 = c130 x F130 = 0.42 x 4 = 1.68 base up @ 130.
These two prisms are now to be constructed to scale on the graph (P40 = OX and P130 = OY) in order to compound them into the single resultant prism, PR, represented by the length OZ.
By measurement, PR = 4.8Δ base up @ 60½.
Finally, resolving PR into vertical and horizontal components, PV (= OV) and PH (= OH),
we find:
PV = 4.2Δ base up and PH = 2.4Δ base in.
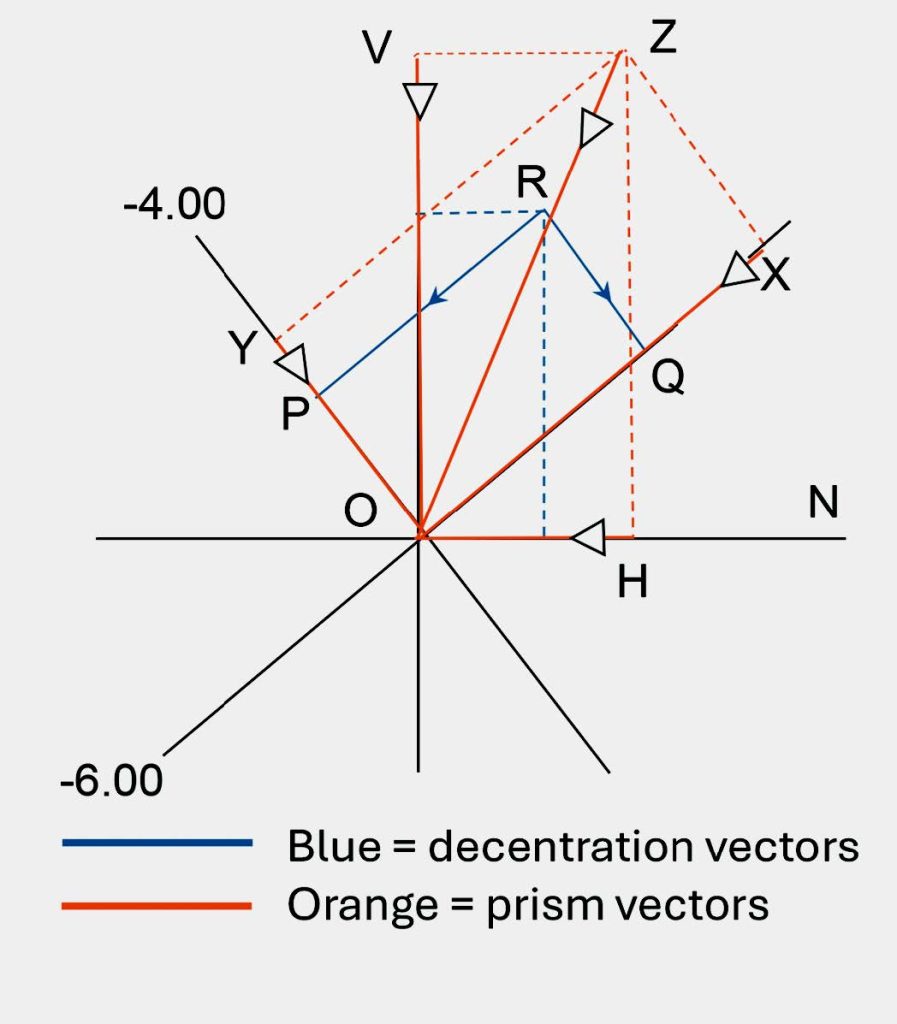
FIGURE 1 – PRISMATIC EFFECT AT A POINT 8MM ABOVE AND 3MM INWARDS FROM OC OF LENS, R -6.00 / +2.00 X 40
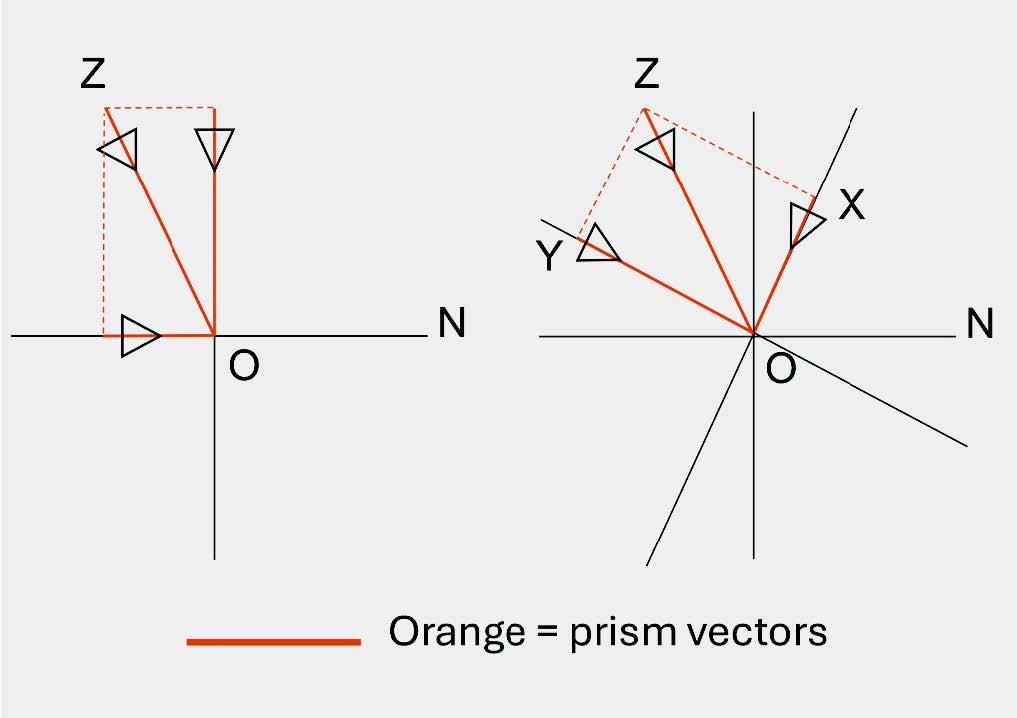
FIGURE 2 – PRISMATIC EFFECT PRODUCED BY DECENTERING THE LENS, L -2.00 / +4.00 X 45, 10MM INWARDS
EXAMPLE (II):
Find the prismatic effects introduced by decentring the lens L -2.00 / +4.00 x 45, 1cm inwards.
The graphical construction is shown in Figure 2. The powers of the lens are -2.00 D along 45 and +2.00 D along 135 and these have been marked upon the principal meridians.
By measurement:
RP = c45 = 0.71cm
and RQ = c135 = 0.71cm.
So, P45 = c45 x F45 = 0.71 x 2 = 1.42Δ base up @ 45,
P135 = c135 x F135 = 0.71 x 2 = 1.42 base up @ 135.
These two prisms can now be constructed on the graph to scale (P45 = OX and P135 = OY)
in order to compound them into the single resultant prism, PR, represented by the length OZ.
By measurement, PR = 2.0Δ base up which represents the total prismatic effect at R.
Note that in this example the lens has been decentred inwards, resulting in a vertical prism!
DECENTRATION TO PRODUCE PRISM – THE GENERAL CASE (GRAPHICAL METHODS)
The graphical construction described above can be reversed to find the decentration necessary to produce a prescribed prismatic effect. The rules for this construction are as follows.
(1) Construct vertical and horizontal meridians and the principal meridians and mark the nasal side of the lens (N).
(2) Draw the prisms to scale with their bases in the correct directions and construct the resultant point, Z.
(3) Resolve the prisms along the principal meridians of the lens (ZX and ZY) by dropping perpendiculars from Z to the principal meridians. Note that the prisms are represented by the lengths, OX and OY and that the positions of X and Y with respect to O, represent their base directions.
(4) Measure OX and OY and calculate the magnitude and the directions of the decentrations necessary to produce them, (OP and OQ).
(5) Compound the decentrations OP and OQ into a single resultant decentration, OR, and resolve OR into vertical and horizontal components, RV and RH. OV represents the required vertical decentration, cV, and OH the required horizontal decentration, cH.
EXAMPLE (III):
Find the vertical and horizontal decentrations required to produce 4Δ base up and 2Δ base out with the lens R +4.50 DS / +2.50 DC x 70.
The principal powers of the lens lie along the 70 and 160 meridians but the prismatic effect which has to be produced is given as vertical and horizontal components, so the first stage of the solution is to compound the given prisms into a single prismatic effect and then to resolve this along the 70 and 160 meridians of the lens.
This construction is shown in Figure 3. Note that the prisms are compounded following the rules given above. At this stage, we are not interested in the actual powers of the lens.
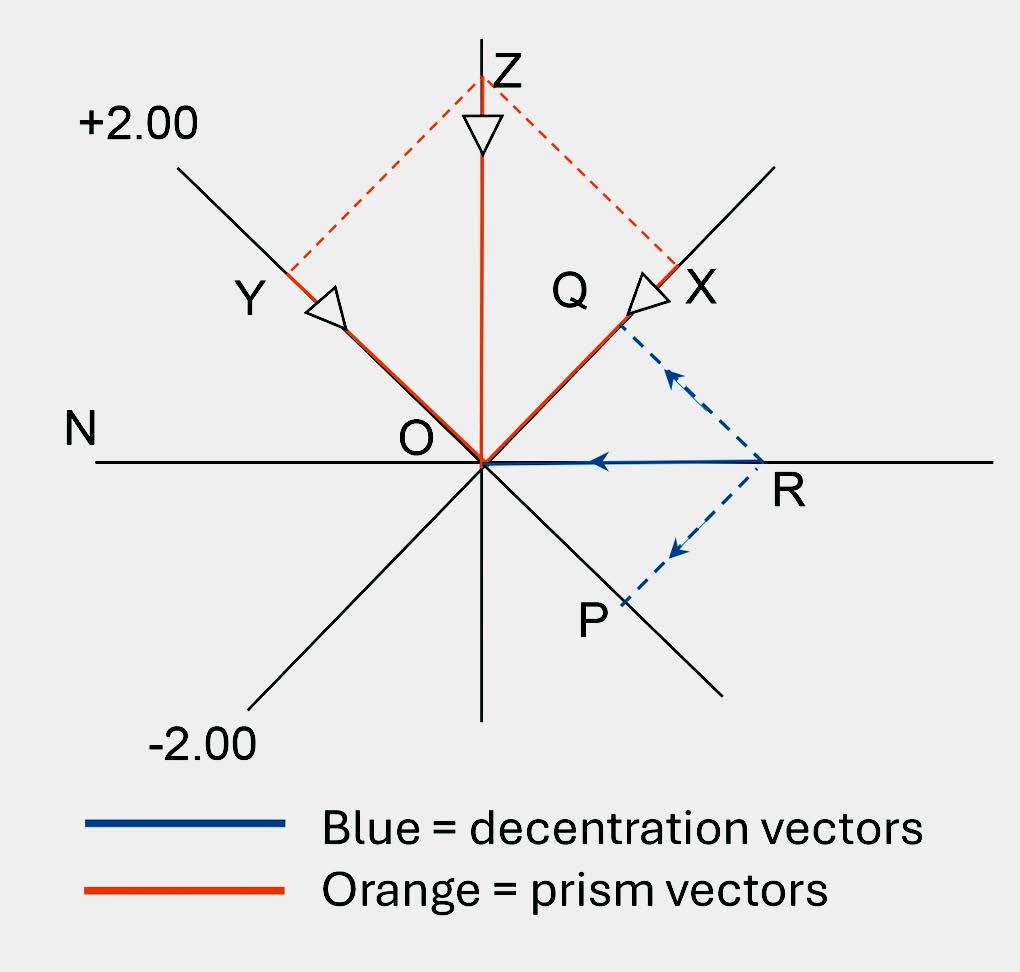
FIGURE 3 – RESOLVING THE PRISMS 4Δ BASE UP & 2Δ BASE OUT ALONG THE 70 AND 160 MERIDIANS
In Figure 3(a), the prisms 4Δ base up and 2Δ base out have been compounded, graphically into the single resultant prism, OZ, which is 4.47Δ base up @ 116.6°.
In Figure 3(b), this single prism, OZ, has been resolved along the 70 and 160 meridians by dropping perpendiculars, ZY and ZX, respectively, onto the principal meridians of the lens.
By measurement:
OX = P70 = 3.1Δ up @ 70,
and OY = P160 = 3.3Δ up @ 160
Note in which direction the base of the two prisms, P70 and P160, lie. The origin, O represents the apex of each prism.
When the prism powers are known along the two principal meridians of the lens, the decentrations required to produce these prisms can be found. Now the powers which lie along the principal meridians, F70 (+4.50) and F160 (+7.00), can be considered.
From the decentration relationship,
c70 = P70 / F70 = 3.1 / 4.50 = 0.69cm = 6.9mm up
@ 70 (since F70 is positive).
c160 = P160 / F160 = 3.3/7.00 = 0.47cm = 4.7mm up
@ 160 (since F160 is positive).
The decentrations c70 (OP) and c160 (OQ) must now be resolved into vertical and horizontal components
In Figure 4(a), the decentration, c70, has been drawn to scale, up along 70 (OP), and c160 drawn to scale, up along 160 (OQ). Completing the rectangle OPRQ, produces the single resultant decentration (OR), which would need to be obtained if the minimum size uncut needed to be determined. By measurement, OR = 8.3mm up @ 104½°.
In Figure 4(b), the single resultant decentration, OR, has been resolved into vertical and horizontal components, OV and OH, by dropping perpendiculars, RV and RH onto the vertical and horizontal meridians respectively.
By measurement, cV (OV), = 8mm up and cH (OH) = 2mm out.
In practice, each step of this solution can be constructed on a single diagram and this single construction where all the separate steps have been combined is shown in Figure 5. The full solution is repeated here.
The powers of the lens are +4.50 D along 70 and +7.00 D along 160 and these have been marked on the construction, together with an indication of the nasal side of the lens.
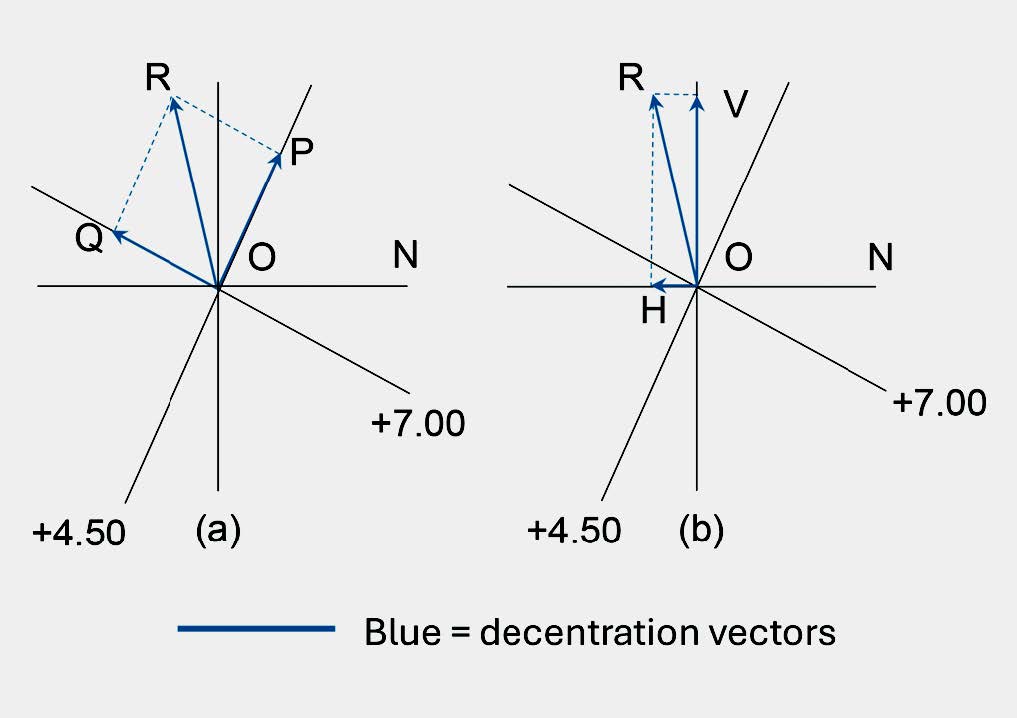
FIGURE 4 – RESOLVING THE DECENTRATIONS INTO VERTICAL AND HORIZONTAL COMPONENTS

FIGURE 5 – COMPLETE, COMBINED CONSTRUCTION FOR EXAMPLE (III), R +4.50/+2.50 X 70 WITH 4Δ BASE UP AND 2Δ BASE OUT
By measurement:
OX = P70 = 3.1Δ up @ 70,
and OY = P160 = 3.3Δ up @ 160
c70 = P70 / F70 = 3.1/4.50 = 0.69cm = 6.9mm up
@ 70 (since F70 is positive).
c160 = P160 / F160 = 3.3/7.00 = 0.47cm = 4.7mm up
@ 160 (since F160 is positive).
The decentrations c70 (OP) and c160 (OQ) can now be constructed to scale on the graph. Note that the scale used to compound the decentrations need not be the same as that used to construct the prisms. The most convenient scale should be chosen.
Completing the rectangle OPRQ, by measurement, OR= 8.3mm up @ 104½ and resolving OR into vertical and horizontal components, cV (OV), and cH (OH), we find cV = 8mm up and cH = 2mm out.
… to be continued
In 1965, the author published a new method for finding the prismatic effect at any point on a lens. The method has the advantage that the graphical work involved is kept to an absolute minimum, accomplished by the fact that the prismatic effect of a spherical lens can usually be determined by simple mental arithmetic, and it is then only necessary to consider the prismatic effect introduced by a plano-cylinder.
A simpler method for finding the prism exerted by a plano-cylinder is shown in Figure 1 which represents a plano-cylinder with its axis inclined at an angle, θ, to the horizontal meridian. Assume that the cylinder is positive and lies before the right eye. It is required to calculate the prismatic effect at the point, R. Note that in addition to the origin, only the cylinder axis has been drawn along its prescribed direction and that the perpendicular distance of point R from the cylinder axis, PR, has been resolved into vertical and horizontal components, PQ and QR, respectively. The vertical prismatic effect at R due to the cylinder is then, the product of PQ in cm and the power of the cylinder and the horizontal prismatic effect at R is the product of QR in cm and the power of the cylinder.
The base direction of the prismatic effect exerted by the cylinder can be found by considering the position of point P with respect to the position of the point, R, at which the prismatic effect is to be found. If the cylinder is positive, point P represents the position of the prism base. In Figure 1, point P clearly lies above the point R and so the vertical component would be base up.
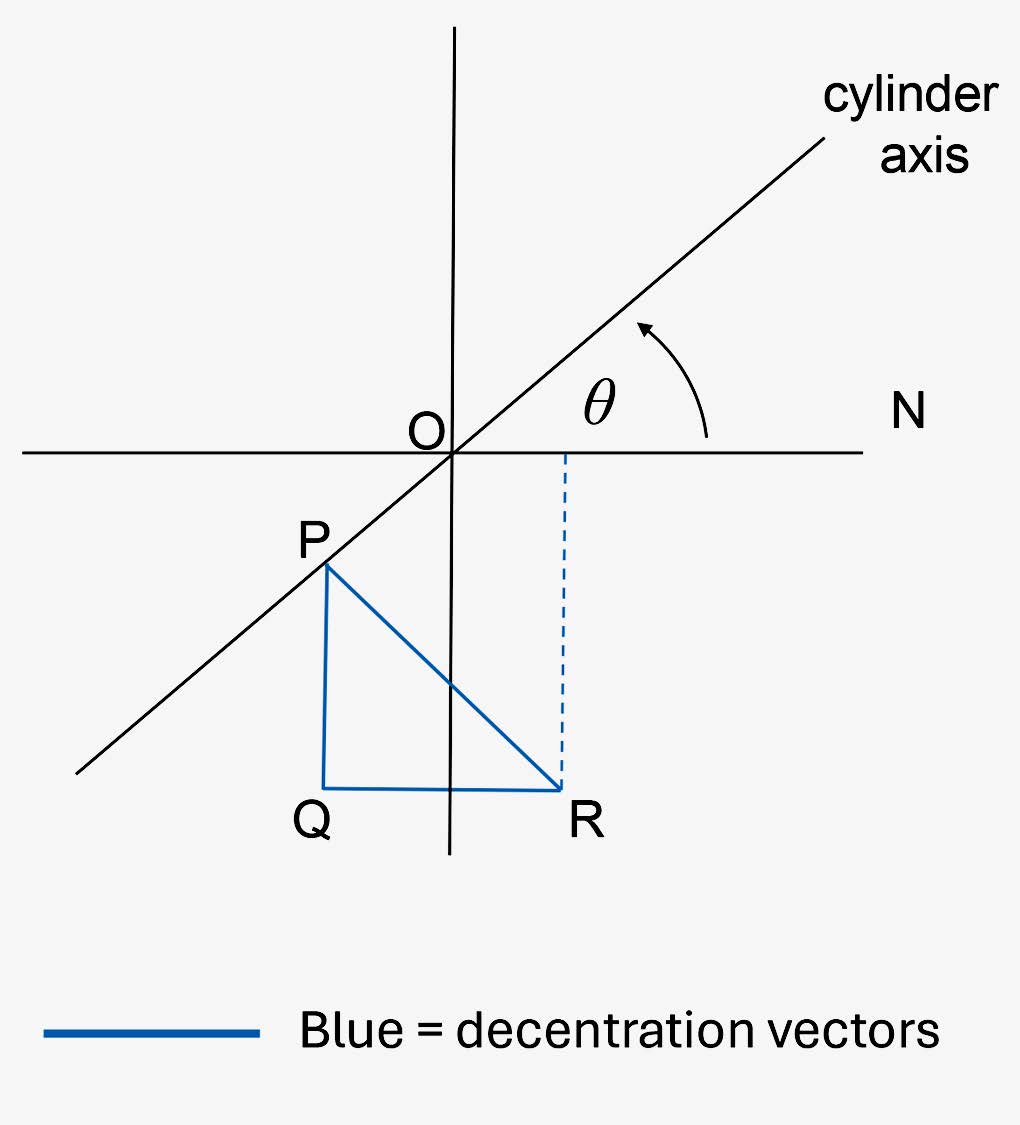
FIGURE 1 – AUTHOR’S METHOD FOR FINDING PRISMATIC EFFECT DUE TO A PLANO-CYLINDER. IF THE CYLINDER IS POSITIVE, P WOULD REPRESENT THE POSITION OF THE PRISM BASE. IF THE CYLINDER IS NEGATIVE, P WOULD REPRESENT THE POSITION OF THE PRISM APEX AND THE BASE WOULD LIE IN THE OPPOSITE DIRECTION.
If the cylinder is negative, then P represents the position of the prism apex and the base lies in the opposite direction.
For example, in Figure 1, assuming the cylinder is positive and is mounted before the right eye, point P lies upwards and outwards with respect to point R. In the case of a plus cylinder, P represents the position of the prism base, so the prismatic effect exerted by the cylinder is base up and out.
If the cylinder had been negative, point P would represent the position of the prism apex and since this lies upwards and outwards from point R, the base direction would be down and in.
THE RULES FOR THIS SIMPLIFIED CONSTRUCTION ARE AS FOLLOWS.
1) Construct an origin and mark the nasal side.
2) Draw the cylinder axis along its prescribed meridian.
3) Mark the position of the point at which the prismatic effect is to be found to scale, point R in Figure 1 (use a 10x scale if possible) and drop a perpendicular from R to the cylinder axis meeting it at P.
4) Resolve the perpendicular, PR, into vertical and horizontal components PQ and QR respectively.
5) The vertical prismatic effect at R is then the product of PQ, measured in cm, and the power of the cylinder and the horizontal prismatic effect at point R is QR measured in cm, and the power of the cylinder.
6) Determine the prism base directions from the following: If the cylinder is positive in sign, point P represents the position of the prism base and if the cylinder is negative in sign, point P represents the position of the prism apex.
The application of this method is illustrated in the following examples, the first of which was given in the last part of this series2.
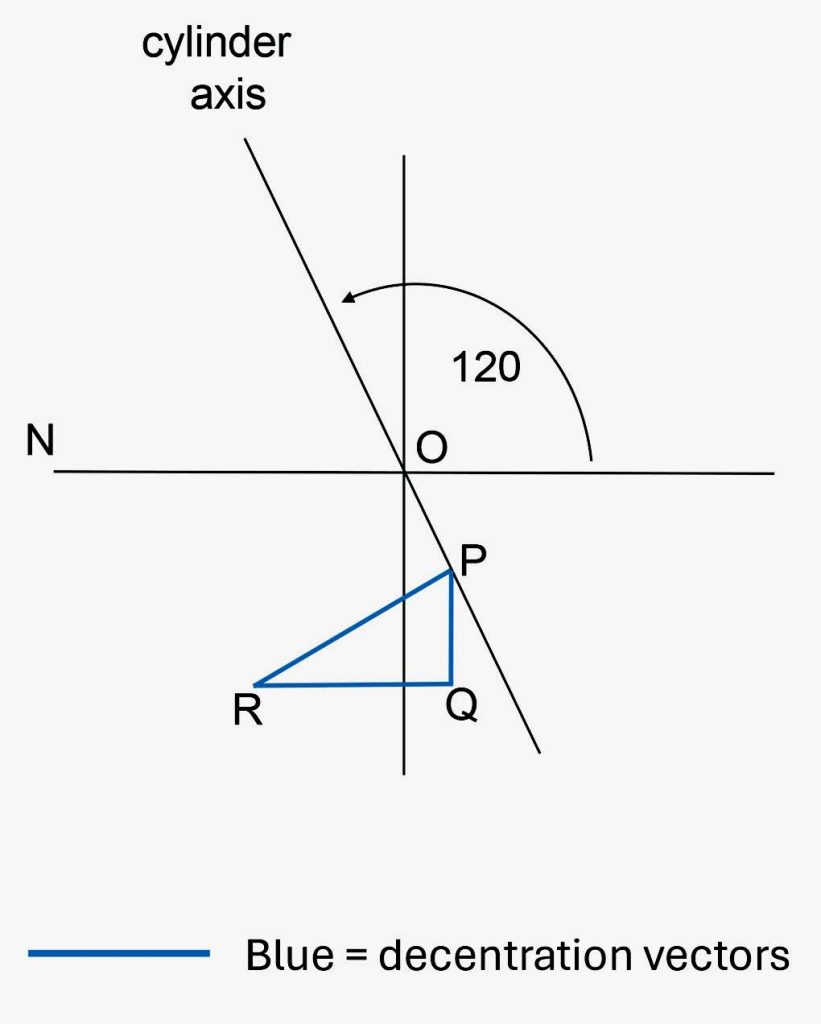
FIGURE 2 – PRISMATIC EFFECT AT A POINT 6MM BELOW AND 4MM INWARDS FROM OC OF LENS, L +2.00/+2.00 X 120. THE CYLINDER IS POSITIVE AND P LIES ABOVE AND OUTWARDS FROM R SO THE BASE DIRECTION OF THE PRISM AT R IS UP AND OUT.
EXAMPLE (I):
Find the prismatic effects at a point 6mm below and 4mm inwards from the optical centre of the lens:
L +2.00 DS/+2.00 DC x 120. (See Figure 2 for graphical construction for the plano-cylinder, +2.00 DC x 120).
The prismatic effect due to the sphere = cV x Fsph and cH x Fsph which is 0.6 x 2.00 = 1.2Δ base up and 0.4 x 2.00 = 0.8Δ base out.
The prismatic effect exerted by the cylinder is found from the graphical construction shown in Figure 2.
By measurement, PQ = 0.32cm and QR = 0.55cm.
The vertical prism due to the cylinder is PQ x Fcyl = 0.32 x 2.00 = 0.64Δ base up
The horizontal prism due to the cylinder is QR x Fcyl = 0.55 x 2.00 = 1.1Δ base out.
Adding the prism due to the sphere we find:
PV = 1.2 + 0.64 = 1.84Δ base up and
PH = 0.8 + 1.1 = 1.90Δ base out.
EXAMPLE (II):
Find the prismatic effects at a point 8mm above and 3mm inwards from the optical centre of the lens R – 6.00 DS/+2.00 DC x 40.
The prismatic effect due to the sphere = cV x Fsph and cH x Fsph which is 0.8 x 6.00 = 4.8Δ base up and 0.3 x 6.00 = 1.8Δ base in.
The prismatic effect exerted by the cylinder is found from the graphical construction shown in Figure 3.
By measurement, PQ = 0.32cm and QR = 0.27cm.
The vertical prism due to the cylinder is PQ x Fcyl = 0.32 x 2.00 = 0.64Δ base down.
And the horizontal prism due to the cylinder is QR x Fcyl = 0.27 x 2.00 = 0.54Δ base in.
Adding the prism due to the sphere we find:
PV = 4.8Δ up + 0.64Δ down = 4.16Δ base up
PH = 1.8Δ in + 0.54Δ in = 2.34Δ base in.
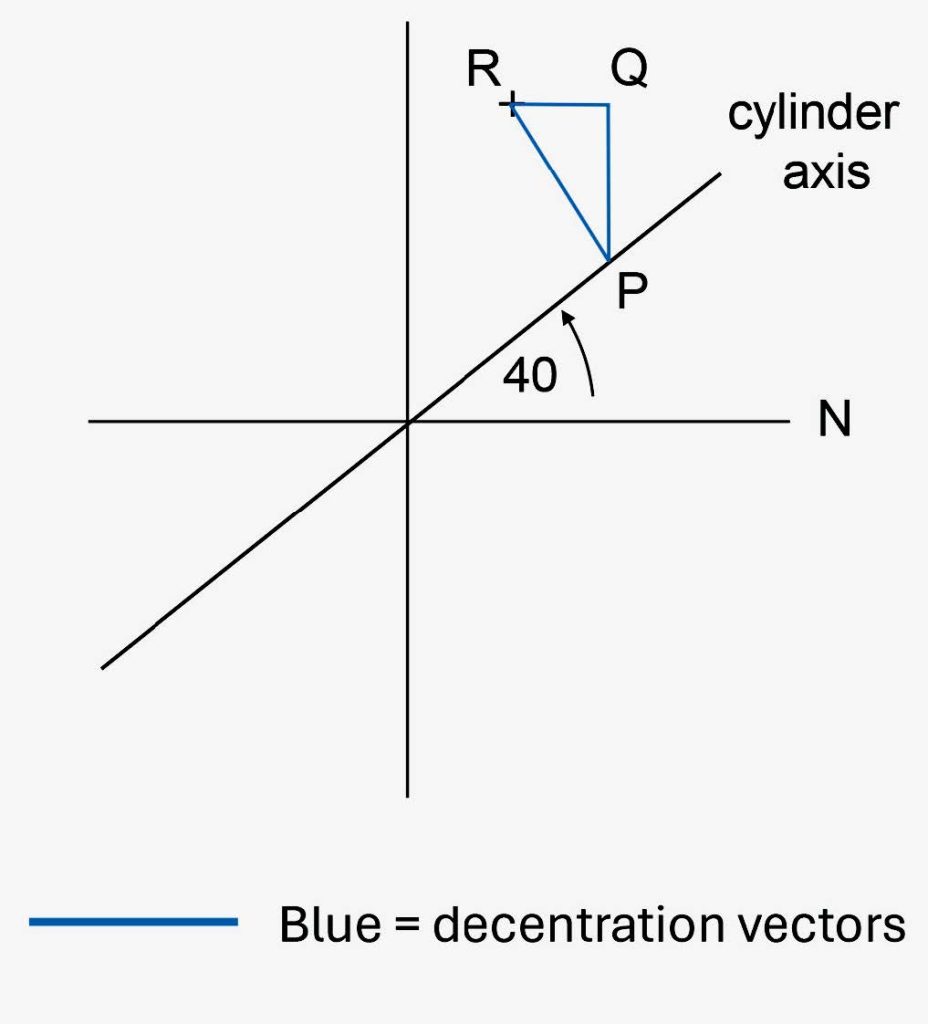
FIGURE 3 – PRISMATIC EFFECT AT A POINT 8MM UP AND 3MM IN FROM THE OPTICAL CENTRE OF THE LENS R – 6.00 DS/+2.00 DC X 40.
THE CYLINDER IS POSITIVE AND P LIES BELOW AND INWARDS FROM R SO THE BASE DIRECTION OF THE PRISM AT R IS DOWN AND IN.
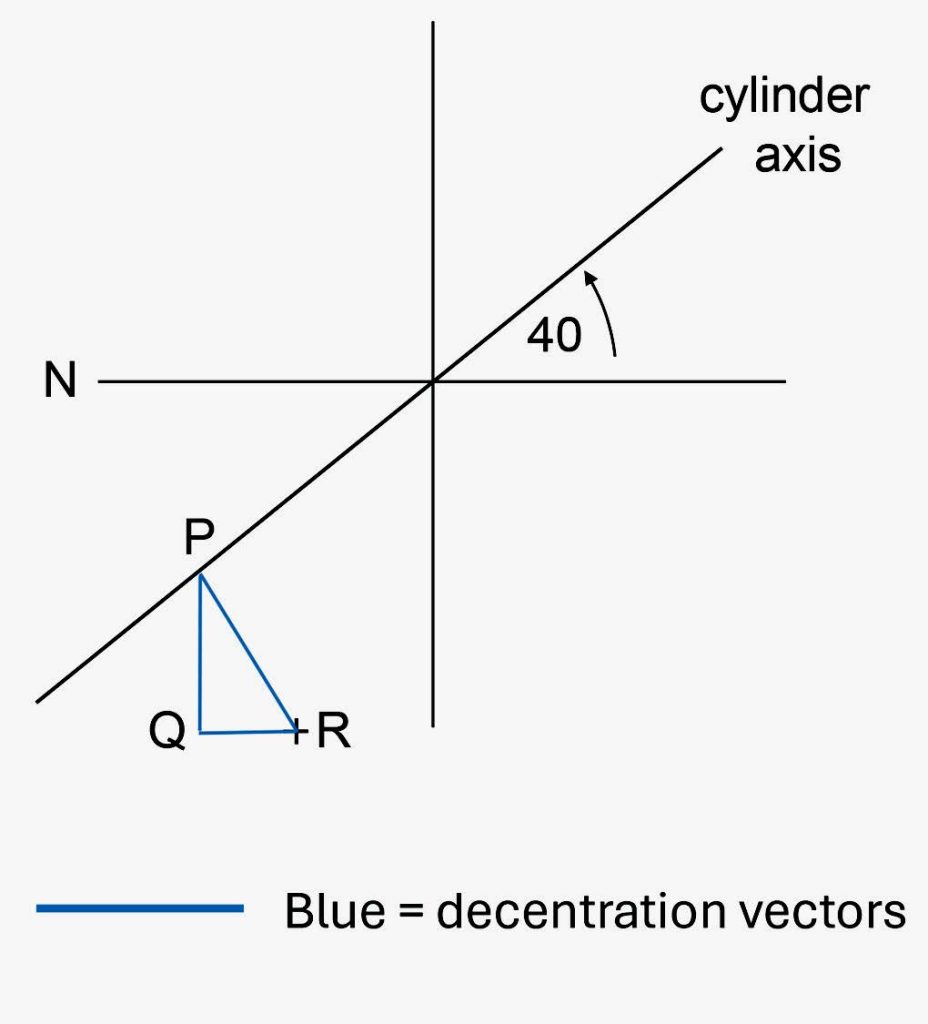
FIGURE 4 – PRISMATIC EFFECT AT A POINT 10MM BELOW AND 2MM IN FROM THE OPTICAL CENTRE OF THE LENS
L -4.00 DS/-2.00 DC X 40.
THE CYLINDER IS NEGATIVE AND P LIES ABOVE AND INWARDS FROM R SO THE BASE DIRECTION OF THE PRISM AT R IS DOWN AND OUT.
EXAMPLE (III):
Find the prismatic effects at a point 10mm below and 4mm inwards from the optical centre of the lens
L – 4.00 DS/-2.00 DC x 40.
The prismatic effect due to the sphere = cV x Fsph and cH x Fsph which is 1.0 x 4.00 = 4.0Δ base down and 0.4 x 4.00 = 1.6Δ base in.
The prismatic effect exerted by the cylinder is found from the graphical construction shown in Figure 4.
By measurement, PQ = 0.39cm and QR = 0.33cm.
The vertical prism due to the cylinder is PQ x Fcyl = 0.39 x 2.00 = 0.78Δ base down
the horizontal prism due to the cylinder is QR x Fcyl = 0.33 x 2.00 = 0.66Δ base out.
Adding the prism due to the sphere we find:
PV = 4.0Δ down + 0.78Δ down = 4.78Δ base down
PH = 1.6Δ in + 0.66Δ out = 0.94Δ base in.
In the final part of this series a purely analytical solution for finding the prismatic effect at any point on a lens will be explained.
REFERENCES
It is of interest to establish formulae in order to be able to calculate and analyse prismatic effects. Such formulae are, of course, essential in order to program computers to be able to calculate the prism necessary to shift the optical centre during surfacing instruction. These formulae require us to formulate a sign convention which informs upon the correct base direction and the direction of decentration. Also, a symmetrical axis notation must be chosen to enable the formulae to work equally for the right and left eyes.
We look first at the sign conventions1. The one chosen for the axis notation is the Binasal convention illustrated in Figure 1. The right eye notation is exactly the same as Standard notation but the left eye directions commence at the nasal side of the lens. To convert left eye axes to Binasal notation the axis in Standard notation is simply subtracted from 180 (Figure 1). The convention chosen for decentrations is also illustrated in Figure 1 . Decentration upwards and outwards is positive. This convention is chosen because the most common problem which occurs involving the calculation of prismatic effects, apart from providing prism-to-cut, is that of finding the prismatic effect in the near visual zones of a pair of lenses.
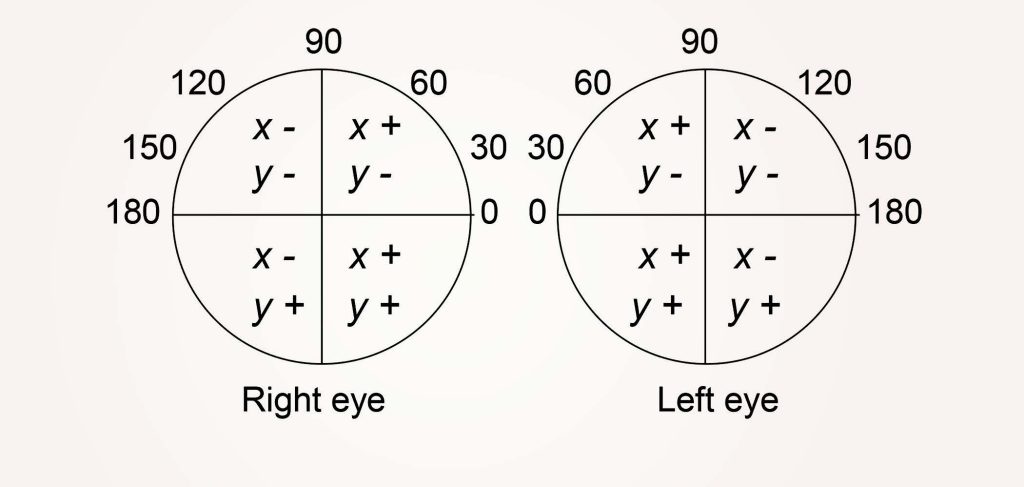
FIGURE 1 – BINASAL AXIS NOTATION AND SIGN CONVENTION FOR DECENTRATIONS, X AND Y.
The expressions for the prismatic effect at any point on a lens can be derived from Figure 2.
Note that the lower, nasal, quadrants of each eye are the all-positive quadrants, the optical centre of each lens is assumed to lie at the origins of the notation for each eye so that decentration upwards and outwards is reckoned positive.
Figure 2 represents the front surface of an astigmatic lens. O is the optical centre of the lens. It is required to calculate the prismatic effect at the point R.
Let: S = the power of the spherical component
C = the power of the cylindrical component
θ = the axis direction in Binasal notation x = the horizontal decentration of the OC y = the vertical decentration of the OC PV = the vertical prismatic effect at R
PH = the horizontal prismatic effect at R
The vertical prismatic effect at R due to the sphere is simply, y.S and the horizontal prismatic effect at R due to the sphere is simply, x.S.
The prismatic effect at R due to the cylindrical component of the lens is the product of the perpendicular distance of R from the cylinder axis, measured in cm, and the power of the cylinder (PR x C in Figure 2), the prism base lying along PR.
From Figure 2, PR = (y + z) cos θ
where z = x tan θ.
Hence, PR = y cos θ + x tan θ cos θ
= y cos θ + x sin θ.
Now the vertical prismatic effect at R due to the cylinder is
C x PQ or C x PR cos θ = C cos θ (x sin θ + y cos θ) Adding the prism due to the sphere, we have:
PV = y.S + C cos θ (x sin θ + y cos θ).
PV will be base up when its sign is positive and base down when its sign is negative.
The horizontal prismatic effect at R due to the cylinder is
C x QR or C x PR sin θ = C sin θ (x sin θ + y cos θ). Adding the prism due to the sphere, we have:
PH = x.S + C sin θ (x sin θ + y cos θ).
PH will be base out when its sign is positive and base in when its sign is negative.
EXAMPLE
Find the vertical and horizontal prismatic effects at a point 11 mm below and 2½ mm inwards from the optical centre of the lens
R +6.00/-3.00 x 140.
We have:
S = +6, C = -3, θ = 140, x = +0.25, y = +1.1
PV = y.S + C cos θ (x sin θ + y cos θ)
= 1.1 x 6 – 3 cos 140 (0.25 sin 140 + 1.1 cos 140)
= +5.03Δ or 5.03 base up since PV is positive.
PH = x.S + C sin θ (x sin θ + y cos θ)
= 0.25 x 6 – 3 sin 140 (0.25 sin 140 + 1.1 cos 140)
= +2.81Δ or 2.81 base out since PV is positive.
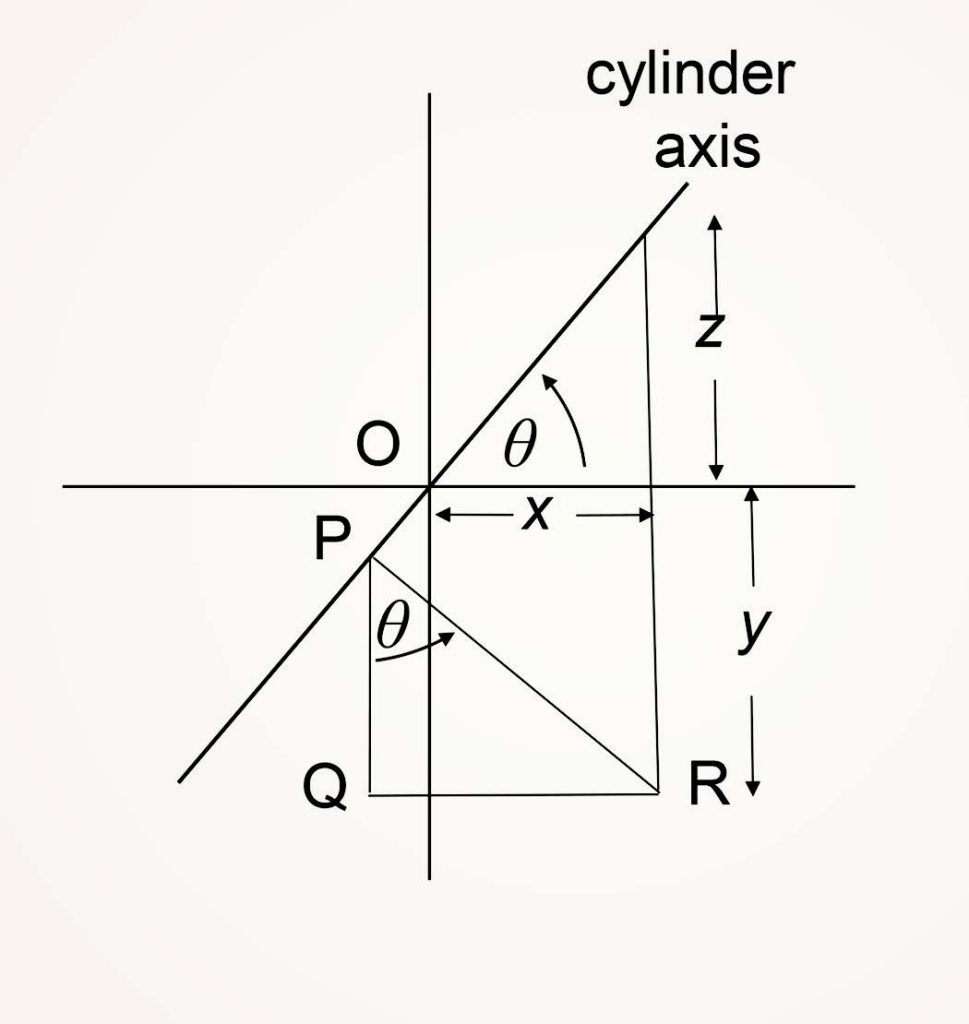
FIGURE 2 – PRISMATIC EFFECT
AT POINT R
These formulae can be transformed to find the vertical and horizontal decentrations (y and x) required to produce a prescribed prismatic effect, PV and/or PH. The same sign convention is used.
We have, from above, by expansion:
PV = y (S + C cos2 θ) + x C sin θ cos θ
and PH = y C sin θ cos θ + x (S + C sin2 θ).
Solving this pair of simultaneous equations we find
y = PV (S + C sin2 θ) – PH C sin θ cos θ / S (S + C) (decentre up when y is positive),
and x = PH (S + C cos2 θ) – Pv C sin θ cos θ / S (S + C)
(decentre out when x is positive).
REFERENCE
Jalie M (2021), Principles of Ophthalmic Lenses (6th Ed.) ABDO, Godmersham.
Prismatic effects can also be found in the general case by the concept of the notional power of a cylinder. This method is popular in the United States even though it is not always applied correctly, for example, when calculating the prism necessary to shift the optical centre during surfacing instruction. The formulae involved use the same sign convention as that derived in Part Six of this series including the use of a symmetrical axis notation to enable the formulae to work equally for the right and left eyes.
Notional cylindrical power is illustrated in Figure 1 which represents a plano-cylinder of power, F, with its axis along the meridian, θ. There is no power along the axis meridian with all the power (F) lying at right angles to the axis meridian. Along a meridian inclined at θ to the cylinder axis, (in Figure 1 it is the horizontal meridian) the notional power of the cylinder1 is F sin2 θ and at right angles to this meridian the notional power of the cylinder is F cos2 θ. For example, if the cylinder depicted in Figure 1 is +3.00 DC x 30, then the notional power in the horizontal meridian is +3.00 x sin2 30 = +0.75, and the power in the vertical meridian is +3.00 x cos2 30 = +2.25 D. Note that the sum of the two notional powers is always equal to the maximum power of the cylinder.
A very useful application of notional cylindrical power is that of finding the prismatic effect at any point on an astigmatic lens. Indeed, correctly applied, the methods about to be described in many cases reduce the problem of prismatic effects exerted by a cylinder to within the realms of mental calculation.
The formulae involved, together with the necessary sign convention have already been given in Part Six of this series and you are advised to read this Part again before proceeding with the following.
It was seen in Part Six, that the vertical and horizontal prismatic effects exerted at any point on a lens (PV and PH respectively) are given by
PV = yS + C cos θ (x sin θ + y cos θ) and PH = xS + C sin θ (x sin θ + y cos θ)
Since the prismatic effect exerted by the sphere can be found separately and simply added to the prism exerted by the cylinder to produce the total solution, it is only necessary to consider the prismatic effects exerted by the cylindrical component, i.e.,
PV = C (x sin θ cos θ + y cos2 θ) and PH = C (x sin2 θ + y sin θ cos θ)
Consider the plano-cylinder of power, F, illustrated in Figure 1. The axis direction of the cylinder (in Binasal notation) is θ. The power of the lens along the meridian, θ, is zero. The power along the meridian (90 + θ) = F.
In the vertical meridian the notional cylindrical power is F cos2 θ and in the horizontal meridian the notional cylindrical power is F sin2 θ. We wish to find the vertical and horizontal prismatic effects at the point R whose position is given with respect to O by the rectangular co-ordinates (x,y).
These effects are PV = C (x sin θ cos θ + y cos2 θ) and PH = C (x sin2 θ + y sin θ cos θ)
Consider the vertical prismatic effect.
Since sin θ = cos θ tan θ, we can write
PV = C (x tan θ cos2 θ + y cos2 θ).
From the geometry of Figure 1, we can see that
z = x tan θ.
Therefore, PV
= C cos2 θ (y + z).
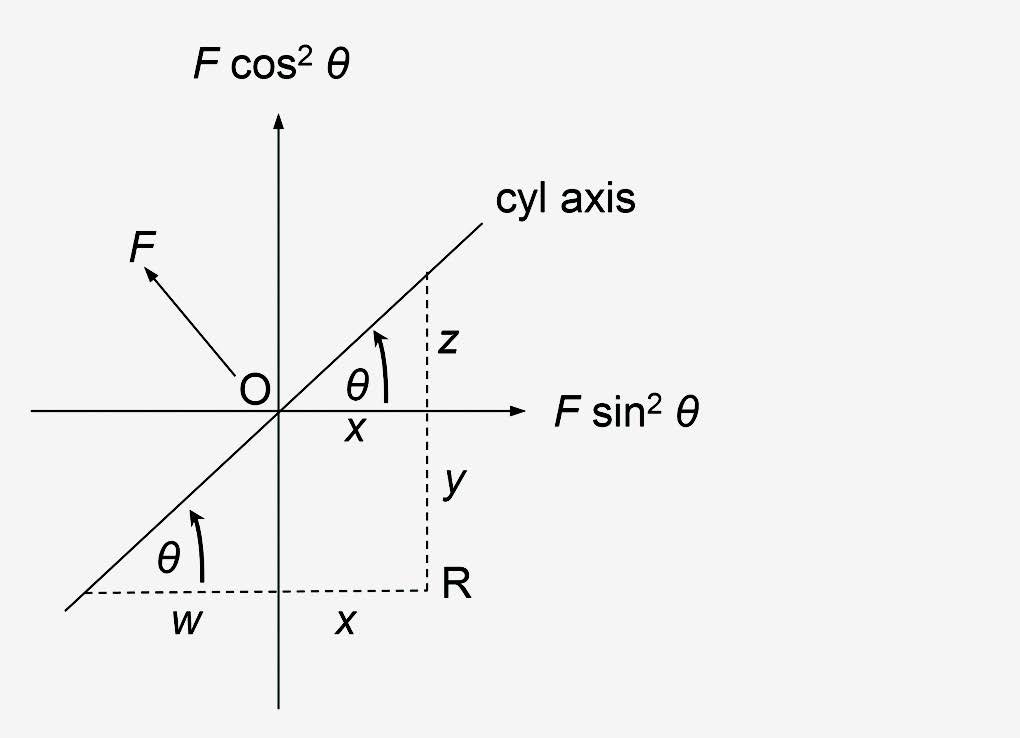
FIGURE 1 – NOTIONAL POWERS OF A PLANO-CYLINDER
Now, C cos2 θ is the notional power of the cylinder in the vertical meridian and it is seen that in order to calculate the prismatic effect in the vertical meridian the notional power of the cylinder must be multiplied by the vertical distance from the point R to the cylinder axis (measured, as usual, in cm). The distance y is normally known, but the distance z must be calculated from z = x tan θ. It will be noticed that when x = 0, z also equals 0 and the vertical prismatic effect is simply y F cos2 θ.
Similarly, in the horizontal meridian it can be seen from the geometry of Figure 1 that y = w tan θ.
Substituting for y, we have PH = C sin2 θ (x + w).
C sin2 θ is the notional power of the cylinder in the horizontal meridian and it is seen that in order to calculate the prismatic effect in the horizontal meridian, the notional power of the cylinder must be multiplied by the horizontal distance from the point R to the cylinder axis (measured in cm). The distance x is normally known, but the distance w must be calculated from w = y cot θ.
It can be seen that when y = 0, w also equals 0 and the horizontal prismatic effect is simply x F sin2 θ.
Before considering the use of these equations, it is worthwhile collecting them together and looking at them in more detail.
We have: PV = C cos2 θ (z + y) where z = x tan θ and PH = C sin2 θ (x + w) where w = y cot θ
Also, when x = 0, PV = y C cos2 θ
and PH = w C sin2 θ.
When y = 0, PV = C cos2 θ and PH = C sin2 θ.
We should not make the mistake of thinking that, when x = 0, there is no horizontal prismatic effect, or that, when y = 0, there is no vertical prismatic effect for it will be recalled from earlier parts of this series that an oblique cylinder produces an oblique prismatic effect which may be resolved into both vertical and horizontal components.
The signs of the distances z and w must also be carefully considered. If we suppose that Figure 1 represents a right eye, then both z and w are positive. Whether these quantities should be added to, or subtracted from, y and x respectively, is most easily decided from a sketch. If we consider the vertical distance (y + z) it can be seen from Figure 1 that (y + z) is greater then y and therefore z must be added to y, but if the cylinder axis were rotated through 90°, then, (y + z) would be less than y and so z would have to be subtracted.
Remember that, in the case of sphero- cylindrical lenses, the prismatic effect exerted by the sphere must be calculated separately and added to the prismatic effect of the cylinder.
EXAMPLE
i) Find the prismatic effect at a point 6mm below and 4mm inwards from the optical centre of the lens
L +2.00 / +2.00 x 120. (see Part 5 for an alternative solution). The graphical construction for the prism due to the cylinder is shown in Figure 2.
We have, S = +2, C = +2, θ = 60 (Binasal notation) y = +0.6, x = +0.4.
The prism due to the sphere is, y S and x S = 0.6 x 2 = 1.2Δ base up and 0.4 x 2 = 0.8Δ base out.
The prism due to the cylinder
PV = C cos2 θ (z + y), where z = x tan θ.
z = 0.4 tan 60 = +0.69
PV = 2 cos2 60 (0.69 + 0.6) = +0.65Δ base up, (since positive).
PH = C sin2 θ (x + w), where w = y cot θ.
w = 0.6 cot 60 = +0.35
PH = 2 sin2 60 (0.4 + 0.35) = +1.13Δ base out, (since positive).
Adding the prism due to the sphere we find
PV = 1.2 + 0.65 = 1.85Δ base up
and PH = 0.8 + 1.13 = 1.93Δ base out.
ii) Find the prismatic effect at a point 11mm below and 2½mm inwards from the optical centre of the lens R +6.00 / -3.00 x 140. The graphical construction for the prism due to the cylinder is shown in Figure 3.
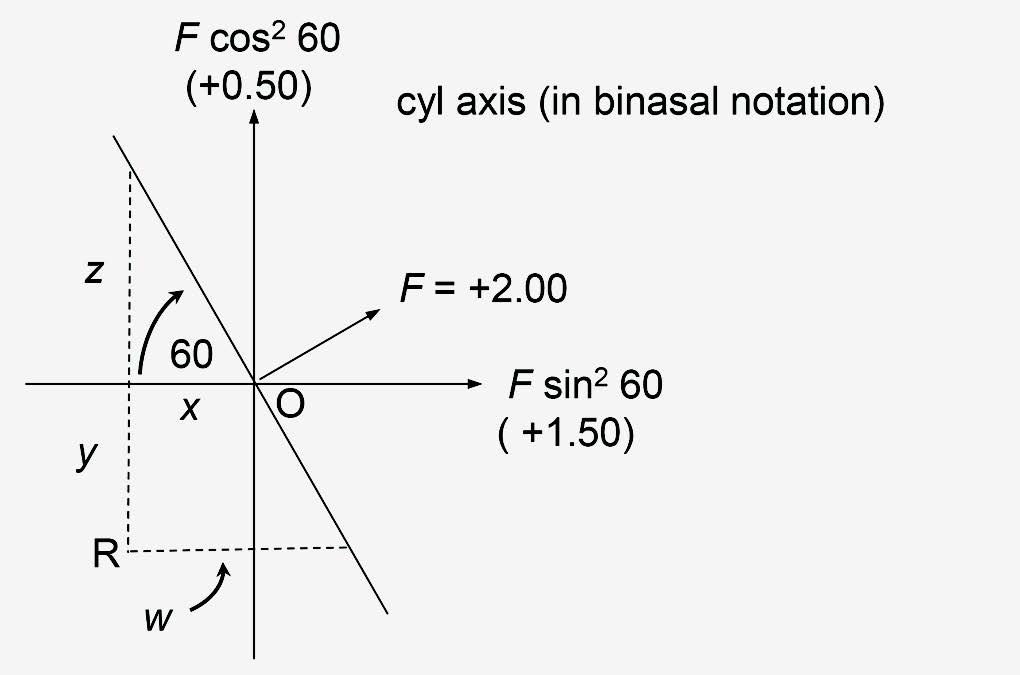
FIGURE 2 – EXAMPLE 1, +2.00/+2.00 X 120 (NOTE IN BINASAL NOTATION, AXIS = 60)
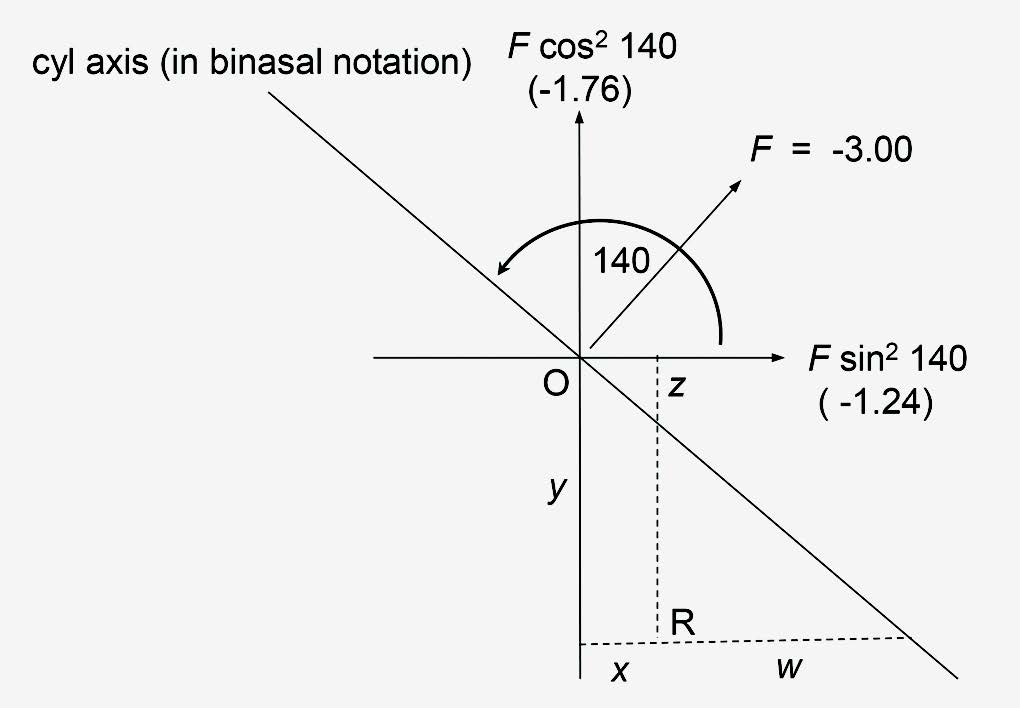
FIGURE 3 – EXAMPLE 2, +6.00/-3.00 X 140 (NOTE IN BINASAL NOTATION, AXIS = 140)
We have S = +6, C = -3, θ = 140 (Binasal notation) y = +1.1, x = +0.25.
The prism due to the sphere is, y S and x S = 1.1 x 6 = 6.6Δ base up and 0.25 x 6 = 0.8Δ base out.
The prism due to the cylinder
PV = C cos2 θ (z + y), where z = x tan θ.
z = 0.25 tan 140 = -0.21
PV = -3 cos2 140 (-0.21 + 1.1) = -1.57Δ base down,
(since negative).
PH = C sin2 θ (x + w), where w = y cot θ.
w = 1.1 cot 140 = -1.31
PH = -3 sin2 140 (0.25 – 1.31) = +1.31Δ base out, (since positive).
Adding the prism due to the sphere we find
PV = 6.6 – 1.57 = 5.03Δ base up
and PH = 1.5 + 1.31 = 2.81Δ base out.
REFERENCE
In dispensing practice, a knowledge of prismatic effects is essential to ensure comfortable binocular vision. Since prismatic effects are dependant upon the power of the lens, any power difference between the eyes will cause them to encounter differential prismatic effects when the eyes rotate away from the optical centres of the lenses. This final part of the series on the prismatic effect of decentration considers these differences and the correct way to centre the lenses in the vertical meridian.
DIFFERENTIAL PRISMATIC EFFECTS
An important application of the decentration relationship is to discover the zones of comfortable vision which exist in any pair of spectacles. We have seen that only when the eye views directly through the optical centre of a lens there is no prismatic deviation introduced by the lens. The eye, however, is not a stationary system but is capable of rotating to view objects through almost any zone on a spectacle lens. The zone or area of the lens which the eye most frequently uses for distance vision is known as the distance visual zone. The centre of this zone, the distance visual point (DVP) is the point at which the dispensing optician places the optical centre of the distance correcting lens. When the optical centres coincide with the DVPs, the lenses are said to be centred. Consider a subject who is wearing a correctly centred pair of spectacle lenses before the eyes. When the subject rotates the eyes to view laterally placed objects, extra-axial points (i.e., points away from the optical centres) on the lenses are being used. Suppose the prescription is +5.00 DS for each eye. The condition where the refractive error in each eye is the same is called isometropia. When the subject rotates the eyes to the right to view through points, say, 5mm to the right of each optical centre, the lenses exert, R 2.5Δ base in and L 2.5Δ base out at these points. Horizontal prisms whose bases are in and out in each eye, of course, neutralise one another.
The effect of this pair, is merely to cause the eyes to rotate together to the right.
When the subject looks through points 8mm above the optical centres, the lenses exert 4Δ base down in each eye. Again there is no difference between these prismatic effects, the eyes being called upon to rotate through equal amounts. However, when the refractive conditions are not the same in each eye, a condition known as anisometropia (or they might even be opposite, e.g., R Myopia L Hypermetropia the condition of antimetropia), the eyes will encounter different amounts of prismatic effect causing unequal rotations. These differences in prismatic effect must be carefully considered, especially in the vertical meridian since, in general, the eyes will not tolerate a vertical difference of more than about 1Δ. If a pair of eyes wearing R +5.00 DS L +2.00 DS, rotate upwards so that the visual axes intersect the lenses 1cm above the optical centres, the lenses introduce the amounts R 5Δ base down and L 2Δ base down. The difference between these prismatic effects is called differential or relative prismatic effect and it is seen that there is 3Δ more base down in the right eye (or, we might say, 3Δ more base up in the left eye). This differential prismatic effect requires the right eye to rotate upwards in relation to the left eye. Fusion would probably be lost and the object under view would be seen double. Generally, anisometropic subjects restrict their visual zones to an area on the lenses where the vertical differential prismatic effect does not exceed 1Δ.
Horizontally, the tolerance is somewhat greater, especially on the convergent side, since the fusional reserves are normally much larger in the horizontal meridian.
Differential prismatic effects are particularly important in near vision. When a subject reads, the head is lowered and the eyes rotated downwards and inwards from the position they occupy for straight-ahead vision. The zone on the lens which is used mainly for near vision is called the near visual zone. The centres of the near visual zones, the near visual points (NVPs) are, on average, 10 to 12 mm below and about 2 to 3 mm to the nasal side of the DVPs (Figure 1). On the basis of the foregoing it can be seen that just 1.00 D of anisometropia in the vertical meridian would produce 1Δ of relative or differential prismatic effect at the centres of the near visual zones. Anisometropes wearing spectacles mainly for near vision would, therefore, require their lenses to be correctly centred in the near visual zones. Alternatively, the normal reading posture must alter, the head being held lower and hence the eyes higher and closer to the optical centres of the lenses. There is no doubt that near vision is more comfortable with correctly centred near vision lenses.
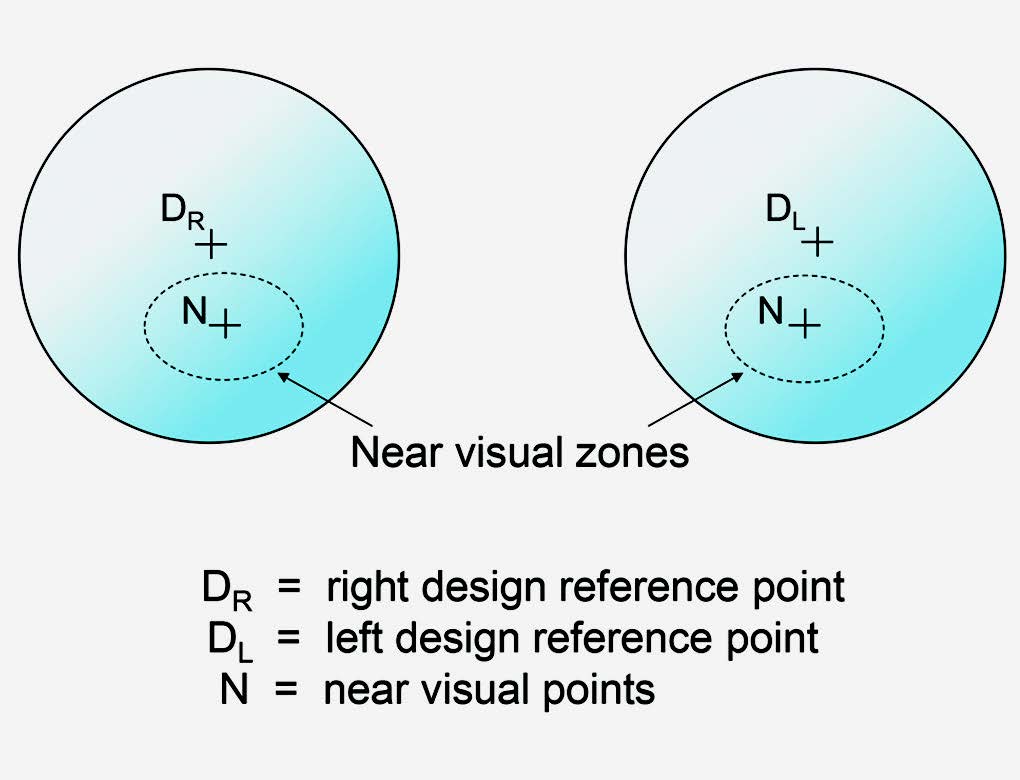
FIGURE 1 – NEAR VISUAL ZONES
The vertical differential prismatic effect at points y cm from the optical centre of a pair of spectacle lenses can be calculated immediately from the prescription without finding the vertical prismatic effect at each point and, hence, the difference. For a pair of spherical lenses of powers, F1 and F2, and assuming that the stronger lens is F1 and the weaker lens F2, the vertical differential prismatic effect is given by
P1 – P2 = δPV = y (F1 – F2) = y δF.
that is, δPV = y δF.
Thus, for the prescription, R +7.00 DS L +4.00 DS, at points 10mm below the optical centres we have δPV = +3Δ R, i.e., 3Δ up R. Or, for the prescription R -2.00 DS L -4.00 DS, at points 8mm below the optical centres, δPV = -1.6Δ L, or 1.6Δ base down L.
With astigmatic lenses, in the vertical meridian only (x = 0) we have (from Part 6).
δPV = y (S1 + C1 cos2 θ1) – y (S2 + C1 cos2 θ2)
Thus for the prescription:
R +2.00 DS / +2.00 DC x 120,
L +1.00 DS / +1.00 DC x 60.
(n.b., θ2, = 120 in Binasal notation), at points 1cm below the optical centres of the lenses we have:
δPV = y (S1 + C1 cos2 θ1) – y (S2 + C1 cos2 θ2)
= 1x(2 + 2 cos2 120) – 1x(1 + 1 cos2 120)
= +1.25Δ or 1.25 base up for the R eye.
In practice, it is of interest to consider the iso-prism zone dimensions for the differential prescription for a pair of lenses. The iso-prism zones then represent the areas on a pair of lenses within which the eyes will not meet a given amount of differential prismatic effect.
The question of differential prismatic effects assumes great importance when considering bifocal and progressive power lenses, since, with these, the eyes are forced to use extra-axial zones of the lens, in order to benefit from the near correction.
SPECTACLE LENS CENTRATION
The point at which the optical centre should be located in the absence of prescribed prism is called the centration point. The horizontal distance between the centration points in a pair of lenses is called the centration distance.
Spectacle lenses are mounted before the eyes in a plane which is approximately parallel to the plane joining the supra-orbital ridge to the chin. This plane is usually inclined at an angle, θ, of between 5° and 15° to the normal to the primary direction of the eye and the angle is referred to as the pantoscopic angle. If the line of the side of the spectacle frame is horizontal, as it often is, the pantoscopic angle is the same as the angle of side. In order for the optical performance of the lens to match that which the designer intended, it is necessary for the optical axis of the lens to pass through the eye’s centre of rotation. This can be achieved by lowering the optical centre of the lens to compensate for the tilted spectacle plane. This is known as satisfying the centre of rotation condition.
The amount by which the optical centre should be lowered, DO, can be deduced from Figure 2. If the pantoscopic angle is denoted by θ, and the distance from the back vertex of the lens to the eye’s centre of rotation by z then the amount by which the optical centre should be lowered, DO is seen to be:
DO = z tan θ.
The dispensing rule, that the optical centre should be lowered by 0.5mm for every 1° of pantoscopic angle, has its origin here. In general, the optical centre of a lens should not be placed directly in front of the centre of the eye’s pupil, but on average some 4 to 5mm below the pupil centre. In practice, this position of the optical centre is often obtained with no specific instruction on the prescription order, simply because modern cosmetic dispensing dictates that the frame occupies a position such that the centre of the pupil lies 4 to 8mm above the horizontal centre line. If the practitioner does not give any instructions to the contrary, it is usual for the prescription house to place the optical centre at its own standard optical centre position which is either on the HCL or 1 to 3 mm above it. This practice has the obvious advantage that the edge thickness at the top and bottom edge of the lens will match more closely.
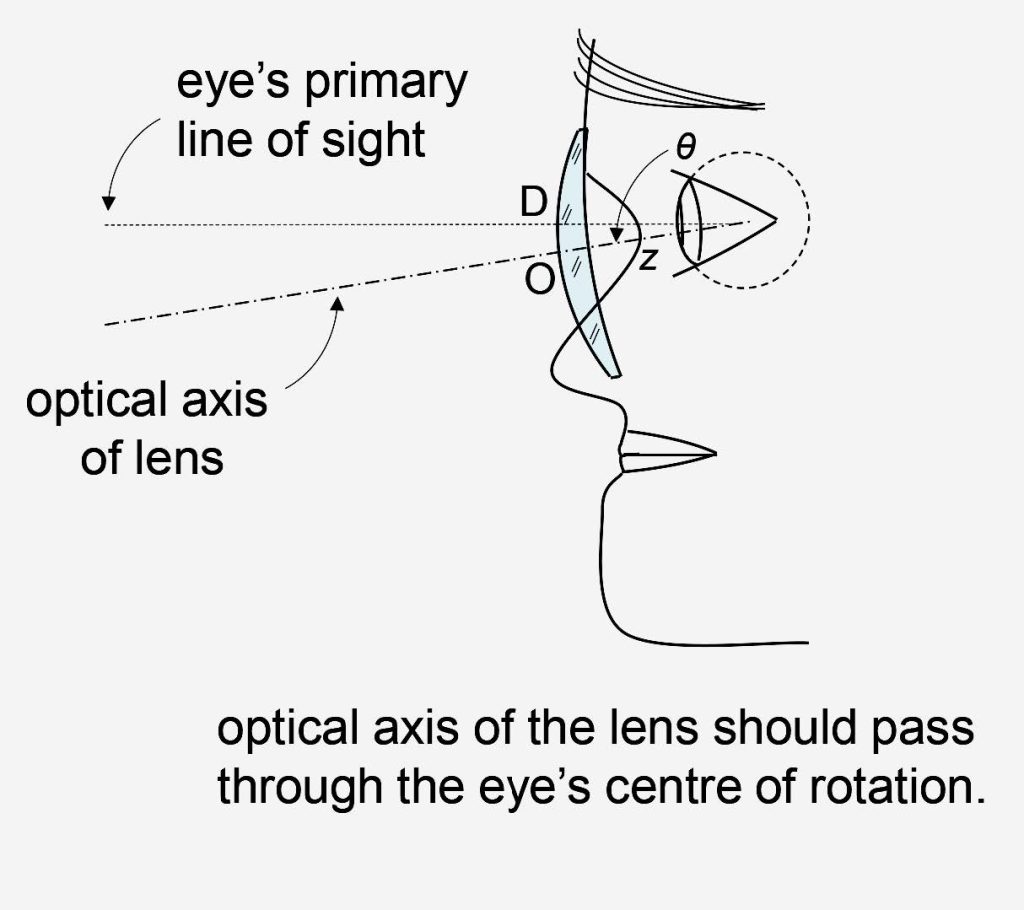
FIGURE 2 – THE CENTRE OF ROTATION CONDITION
In cases of anisometropia, lowering the optical centres may give rise to discomfort since vertical differential prismatic effect will be introduced at the distance visual points. In such cases it would be usual to specify the vertical positions of the optical centres of the lenses. For distance vision they would normally be placed directly in front of the centres of the pupils when the eyes occupy the primary position. In these cases, unless the pantoscopic angle is zero, i.e., the lens is not tilted at all, the wearer cannot benefit fully from the best form principle of the lens. On the other hand, if the lens is mounted perpendicular to the primary direction of sight, the bottom edge of the lens will appear to jut out from the cheek and the cosmetic appearance of the spectacles will suffer.
When the spectacle lens has been correctly centred for distance vision by lowering the optical centre to compensate for the pantoscopic angle, no further vertical decentration of the optical centre is necessary for near vision. This should be obvious from Figure 2 where it can be seen that lowering the optical centre of the lens results in the centre of the distance visual zone lying as far above the optical centre as the centre of the near visual zone lies below the optical centre. In other words, centering the lenses correctly for distance vision in the vertical meridian, centres them correctly for near vision at the same time.
REFERENCE
copyright © 2020-2024 all rights reserved The Indian optician

copyright © 2020-2024 all rights reserved the indian optician
RETURN AND REFUNDS
If for any reason you are not completely satisfied with The Indian Optician magazine subscription, you may claim a full refund of your subscription, by contacting us within 30 days of your transaction processing date for online subscription and print subscription.
CANCELLING SUBSCRIPTION
You may cancel your Subscription at any time during your subscription term. If you choose to cancel your Subscription, please note that we do not issue refunds on magazines already delivered. You may request a refund for all magazines not yet delivered, by contacting us at infotiodel@gmail.com. The amount to be refunded will be a pro rata value based on the number of magazines already issued. Money will be refunded as below:
1) If paid by credit card, refunds will be issued to the original credit card provided at the time of purchase.
2) In case of payment gateway, payments refund will be made to the same account or in the bank account provided by the customer.
We appreciate your interest in our magazine and services. We take special care for the protection of your personal information and sensitive personal data or information. Here, when we refer to “you”, we are referring to the person or entity accessing and/or using the Website. Any information collected, received, possessed, stored, dealt with or handled will be treated in accordance with the Information Technology Act, 2000 and the rules made thereunder and the amended provisions pertaining to electronic documents / records in various statutes as amended by the Information Technology Act, 2000 (“Applicable Law”). Your information will not be disclosed to anyone outside of The Indian Optician, its affiliated or group companies (collectively “TIO” or “we” or “us”), or as otherwise described under this policy (“Privacy Policy”).
This Privacy Policy is published and shall be construed in accordance with the provisions of the Information Technology (Reasonable Security Practices and Procedures and Sensitive Personal Data of Information) Rules, 2011 under Information Technology Act, 2000.
Please read this Privacy Policy carefully. This Privacy Policy is an electronic record in the form of an electronic contract formed under Applicable Law and is a legally binding document between you and TIO. This Privacy Policy does not require any physical, electronic or digital signature.
1. YOUR CONSENT
By using the Website, you indicate that you understand, agree and consent to this Privacy Policy and agree to be bound by the terms and conditions of this Privacy Policy. If you do not agree with the terms of this Privacy Policy, please do not use this Website. By using this website, you expressly and unconditionally consent to the collection, storage, processing, disclosure and transfer of any or all of your information in accordance with this Privacy Policy and in accordance with the provisions of Information Technology Act, 2000. You further agree that such handling of your information shall not cause any loss or wrongful gain to you or any other person.
By providing your contact information, you also consent to be contacted via phone and sms, email or any other modes of communication by TIO. You agree that you are explicitly soliciting communication from TIO on the phone number and email-id provided by you to assist you with required information about TIO magazine and services or as specified herein. In preview of the Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (TRAI) guidelines, you hereby authorise TIO to communicate with you through phone and sms even if your number/numbers is/are registered in the National Do Not Call Registry or www.nccptrai.gov.in
2. COLLECTION OF INFORMATION
From time to time, we may collect, receive, possess, store, deal or handle information from you either directly or through our advertisers and agents. Our primary goal in doing so is to provide you a safe, efficient, smooth and customised experience. This allows us to provide magazine, services and features that most likely meet your needs, and to customize our Website to make your experience safer and easier. More importantly, while doing so we collect information from you that we consider necessary for achieving this purpose.
In general, you can browse the Website without telling us who you are or revealing any information about yourself. Once you give us your information, you are not anonymous to us. We may also combine and aggregate information received from you or our advertisers and business partners through your different interactions with our products and services. Where possible, we indicate which fields are required and which fields are optional. You always have the option to not provide information by choosing to not use the Website.
If you transact with us, we collect some additional information, such as your name, email address, phone numbers and preferences, details of your subscription payment details and tracking information from online payments, cheques or money orders.
If you choose to post messages on our message boards, chat rooms or other message areas or leave feedback, we will collect that information you provide to us. We retain this information as necessary to promote our brands, resolve disputes, provide customer support and troubleshoot problems as permitted by law.
If you send us personal correspondence, such as emails or letters, or if other users or third parties send us correspondence about your activities or postings on the Website, we may record and maintain such information.
We collect personally identifiable information (email address, name, phone number, credit card / debit card / other payment instrument details, etc.) from you when you set up a free account with us. While you can browse some sections of our Website without being a registered member, certain activities (such as placing an order) do require registration. We do use your contact information to send you offers based on your previous orders and your interests.
Any information that is freely available or accessible in public domain or furnished under the Right to Information Act, 2005 or any other law for the time being in force shall not be regarded as personal information for the purposes of this Privacy Policy and we will not be responsible for the same.
3. COOKIES
We may automatically track certain information about you based upon your behaviour on our Website. We use this information to conduct internal research on our users’ demographics, interests, and behavior to better understand, protect and serve our users. This information is compiled and analysed on an aggregated basis. This information may include the URL that you just came from (whether this URL is on our Website or not), which URL you next go to (whether this URL is on our Website or not), your computer browser information, and your IP address.
We use data collection devices such as “cookies” on certain pages of the Website to help analyse our web page flow, measure promotional effectiveness, and promote trust and safety. We offer certain features that are only available through the use of a “cookie”. We also use cookies to allow you to enter your password less frequently during a session. Cookies can also help us provide information that is targeted to your interests. Most cookies are “session cookies”, meaning that they are automatically deleted from your hard drive at the end of a session.
Additionally, you may encounter “cookies” or other similar devices on certain pages of the Website that are placed by third parties. We do not control the use of cookies by third parties. If you choose to buy on the Website, we collect information about your buying behaviour.
A “cookie” is a small piece of information stored by a web server on a web browser or your hard drive so it can be later read back from that browser. Cookies are useful for enabling the browser to remember information specific to a given user. We place both permanent and temporary cookies on your computer’s hard drive. The cookies do not contain any of your personally identifiable information. Any information collected is stored in secure databases protected via a variety of access controls and is treated as confidential information by us. By continuing to browse the Website, you are agreeing to our use of cookies.
4. USE OF DEMOGRAPHIC / PROFILE DATA / YOUR INFORMATION
We use your information to provide the products and services you request, to manage your orders and respond to any other requests you may have. To the extent, we use your information to market to you, we will provide you the ability to opt-out of such uses or alternatively, you may inform us in writing (in the manner set out in Section 8 below) that you are not interested in receiving details of any offers.
We use your personal information to resolve disputes, troubleshoot problems, help promote a safe service, collect money, measure consumer interest in products and services, inform you about online and offline offers, products, services, events, research, news and updates, customise your experience, detect and protect us against error, fraud and other criminal activity, enforce our terms and conditions, and as otherwise described to you at the time of collection.
In our efforts to continually improve our product and service offerings, we collect and analyse demographic and profile data about our users’ activity on our Website. Wherever possible or required by Applicable Law, such information processing activities are carried out on an anonymised or pseudonymised basis.
We identify and use your IP address to help diagnose problems with our server, and to administer our Website. Your IP address is also used to help identify you and to gather broad demographic information.
We will occasionally ask you to complete optional online surveys. These surveys may ask you for contact information and demographic information (like zip code, age, or income level). We use this data to tailor your experience at our Website, providing you with content that we think you might be interested in and to display content according to your preferences.
5. SHARING OF PERSONAL INFORMATION
We may share your personal information with our other corporate entities and affiliates. Should this happen, we ensure that these corporate entities and affiliates who handle your information comply with the Applicable Laws and this Privacy Policy. These entities and affiliates may market to you as a result of such sharing, unless you explicitly opt-out, in the manner set out herein.
We may disclose information to third parties who provide us with services, for instance those handling marketing communications on our behalf. When data is disclosed to any third party every precaution will be taken to ensure that any data provided is handled safely and securely by such third-party organisation in compliance with the Applicable Law. You may inform us in writing (in the manner set out in Section 8 below) that your information is not to be disclosed to third parties for their marketing and advertising purposes.
We may disclose information if required to do so by law or in the good faith belief that such disclosure is reasonably necessary to respond to subpoenas, court orders, or other legal process. We may disclose information to law enforcement offices, third party rights owners, or to prevent, detect, mitigate, and investigate fraudulent or illegal activities related to our products and services or others in the good faith belief that such disclosure is reasonably necessary to enforce our Terms or Privacy Policy, respond to claims that an advertisement, posting or other content violates the rights of a third party, or protect the rights, property or personal safety of our users or the general public.
We and our affiliates will share some or all of your information with another business entity should we (or our assets) plan to merge with, or be acquired by that business entity, or re-organization, amalgamation, restructuring of business. Should such a transaction occur that other business entity (or the new combined entity) will be required to follow this Privacy Policy with respect to your information.
6. DATA PROTECTION
Our Website has stringent security measures in place to protect the loss, misuse, and alteration of the information under our control. Any information that you choose to provide us about yourself may be held on secure computer servers at locations within or outside India. Once your information is in our possession we adhere to strict security guidelines, protecting it against unauthorised access. We and any company or organisation who provide us with services will have in place appropriate technical and security measures to prevent unauthorized or unlawful access to or accidental loss of or destruction or damage to your information. We aim to ensure that the information stored will be accurate, relevant and not excessive, though you should ensure that you notify us of any changes in circumstances (such as a change of address) so we can update our records accordingly. We will keep the data up to date and not retain your information longer than is necessary. We will keep data securely to prevent unauthorised access by other people.
We will not sell any identifiable information about you to any third party without your consent. We may share generalised information about behaviour patterns with partners or other parties in such a way that an individual customer can never be identified. Wherever possible or required by Applicable Law, information processing activities are carried out on an anonymised or pseudonymised basis.
7. LINKS TO OTHER SITES
Our Website may include links to other websites that may collect information about you. These websites are not covered by this Privacy Policy and you should ensure that you review the privacy policy of each of these sites before continuing to use them. TIO is not responsible for the privacy practices or the content of those linked websites.
8. OPT-OUT
You always have the option to not provide your information by choosing to not use the Website. You also have the right to ask us to not use your information for marketing purposes or send you offers based on your previous orders and your interests or share your information with third parties for their marketing and advertising purposes by sending an email to us at any time at the e-mail : infotiodel@gmail.com
9. DISCLAIMER
The downloads from this Website have been thoroughly scanned and tested at all stages of production, but, as with all downloads, we recommend that you run a virus check before use. We also recommend that you have an up-to-date backup of your hard disk before using the downloaded content. We cannot accept responsibility for any disruption, damage and/or loss of data on your data or computer system that may occur while using the downloaded content.
This Website should not be regarded as an infallible guide to our products and services, nor does it constitute an offer for the sale of any particular products and services. We are not responsible for any losses you suffer on account of relying on the information contained on this website.
We do not warrant or represent the accuracy or completeness of information provided on this Website. You are advised to verify it before you agree to buy a product from advertisers or service. We do not guarantee that use of this Website will be uninterrupted or error-free, or that the Website and its servers are free of computer viruses or bugs.
10. EXCLUSIONS OF OUR LEGAL LIABILITY
The Website only complies with Indian laws. Information during visits to our Website are processed by us according to the provisions of Applicable Law.
We are strongly committed to protecting the privacy of our customers and we have taken all necessary and reasonable measures to protect the confidentiality of customer information and its transmission through the Website. We shall not be held liable for disclosure of information, in the course of your use of our Website caused by abnormal and unforeseeable circumstances outside our reasonable control, which would have been unavoidable despite all efforts to the contrary, for example delays or failures caused by industrial action, problems with another system or network, third party viruses or malware, mechanical breakdown or data-processing failures.
This Website is intended for residents of India only. All information on this Website is therefore intended only for the Indian market. The information contained on this Website may be altered or amended at any time without prior notification or obligation.
11. NOTICE OF CHANGE
Our privacy policy is subject to change at any time without notice. If we decide to change our Privacy Policy, we will post those changes on this page so that you are always aware of what information we collect, how we use it, and under what circumstances we disclose it. To make sure you are aware of any changes, please review this policy periodically. The effective date of this Privacy Policy, as stated below, indicates the last time this Privacy Policy was revised or materially changed.
12. JURISDICTION
This Privacy Policy shall be governed by and construed in accordance with the laws of India. Disputes arising here from shall be exclusively subject to the jurisdiction of the courts of New Delhi to the exclusion of any other.
EFFECTIVE AS OF FEBRUARY 01, 2021
The tionet.in website (“Website”) is hosted and operated by The Indian Optician (TIO); Registered in A-99 Defence Colony, New Delhi 110024, India.
The information contained on this Website may be altered or amended at any time without prior notification or obligation.
This Website should not be regarded as an infallible guide to The Indian Optician products and services, nor does it constitute an offer for the sale of any particular brand.
Access to, browsing and use of the tionet website, Internet services and mobile device apps (‘App’) are subject to the following Terms and Conditions (‘Terms’). Please read these Terms carefully. Creating an account with tionet (‘we’, ‘us’) or otherwise using any tionet or tionet related service or App will signify that you have read, understood, and agree to be bound by these Terms and to comply with all applicable laws and regulations. These Terms constitute a binding agreement between you and The Indian Optician and affiliates. If you do not agree to these Terms, you may not use this website. THESE TERMS CONTAIN WARRANTY DISCLAIMERS AND OTHER PROVISIONS THAT LIMIT THE LIABILITY OF TIONET, SO PLEASE READ THESE TERMS IN THEIR ENTIRETY. tionet reserves the right to immediately terminate your access to the website, service or tionet related app, if you do not comply with this agreement. The tionet website, Internet services and mobile device apps collectively constitute the ‘Service’. This Service is owned and operated by The Indian Optician. The Service includes the website tionet.in and the App that provides you the capability to order, subscribe the magazines, publication related content (collectively known as ‘Publications’) and to have these digital versions of the Publications delivered to you.
a. Certain portions of the Service are available only to individuals who have registered with and obtained a password from tionet. By registering with tionet, you certify that you are at least 18 years of age. While registering with tionet, you should provide true and accurate data which includes that of your geographical location, personal details, billing information, etc. The accountability for maintaining and updating this data lies solely with you. tionet reserves the right for terminating the account for untrue or inaccurate data at any time if found or proved. The responsibility for maintaining the confidentiality of the password and the account information rests entirely with you. You agree to immediately notify tionet of any unauthorized use of your password or account or any other breach of security.
b. You will maintain and promptly update that information to keep it true, accurate, current and complete. You are responsible for maintaining the confidentiality of your account and password and for restricting access to your computer, and you agree to accept responsibility for all activities that occur under your account, including the selection and use of all content and services.
c. Without prior written or authorised permission from tionet, you should not modify, copy, distribute or sell any content obtained from tionet as everything published here is the proprietary property of tionet or its licensors. As such unauthorised use may also violate applicable laws including copyright and trademark laws, tionet strictly prohibits these and will terminate your access and account if any such illegal activity is proved or detected. You should also stand liable for the damages caused by these unauthorised activities. Except as permitted by the Publication’s lawful owner, you acknowledge that you do not acquire any ownership rights by downloading Publications accessed through the Service. Except as explicitly required under copyright law or permitted by the features of the Service you may not modify, reverse engineer, publish, transmit, display, participate in the transfer or sale, create derivative works of, or in any way commercially exploit or provide to a third party the content of the App, the Publications, or any portion of them without the express permission of tionet and the owner of such content. We do not grant you any licenses, express or implied, to the intellectual property of tionet or tionet’s licensors tionet reserves the right to refuse service, terminate accounts, or cancel orders at any time in its sole discretion, including, without limitation, based upon any activity by a subscriber in violation of these Terms or applicable law.
d. You agree not to misrepresent geographical locations, use proxies, use IP spoofing or by any other means to hide the origin of any message you send or purchase you make through the service. You agree not to pretend as any other individual or identity.
e. The Service is controlled, operated and administered by tionet from its offices within the India. If you access the Service from a location outside India, you are responsible for compliance with all local laws that apply to you.
f. tionet reserves the right to modify or discontinue, temporarily or permanently, the Service (or any part thereof) with or without notice at any time. You agree that tionet shall not be liable to you or to any third party for any modification, suspension or discontinuance of the Service.
g. You agree to indemnify tionet, its employees and its affiliates from all claims, demands, actions, damages, costs and liabilities arising out of your use or misuse of the Service.
h. All sales related taxes will be paid by the user as per the taxation norms that may change from time to time based on location of the user. All pricing and tax on the Apple iTunes App will be governed by Apple’s iTunes Terms and Conditions.
i. Your satisfaction is very important to us. However all sales are final and no refunds in full or in part will be issued to you.
j. All subscriptions bought through TIONET are auto renewable. The subscription automatically renews unless auto-renew is turned off at least 24-hours before the end of the current period.
INFORMATION WE COLLECT
A. We collect Personal Information you enter on or through the Service, such as when you create a tionet account, purchase a magazine/subscription, or contact us.
1. When you create The Indian Optician (TIO) account at tionet.in, we collect your Name, Email address, Password and Gender (optional). We collect these basic details so that you can access your subscriptions on multiple devices. Also, when you change your device, these details will help you sync you’re tionet account and get access to your subscriptions.
2. When you purchase a magazine/subscription on our website, we additionally collect your Address (with Pin Code) and Card details in certain scenarios. This is done to validate the transactions and we shall clear such data when validations are no longer required. Please note that we don’t store your card details and they are stored only by the payment gateway.
3. When you contact us, we collect your email address to provide services and answer your queries.
B. When you send gift cards or subscriptions, we may collect the information you provide about the gift recipients, including name and email address. We will use such information to fulfil your requests, provide the relevant service, or for anti-fraud purposes.
C. The Personal Information we collect allows us to respond to your requests, improve our products and services, customize the advertising and content you see, and communicate with you about new products.
D. If you do not want to receive emails from us, you may opt out of Company’s marketing and promotional messaging by changing the ‘Email Preferences’ under ‘My Account’ after logging in to your tionet account. However, while you maintain an account with Company, you will not be able to opt out of emails that send important notices, such as communications about purchases and changes to our terms, conditions, and policies.
E. We also collect data in a form that does not, on its own, permit direct association with any specific individual. We may collect, use, transfer, and disclose non-personally identifying information for any purpose.
F. We receive and store certain types of information whenever you interact with the Service. Company automatically collects information on our server logs from your browser including your Internet Protocol (IP) address, the name and identity of your computer, mobile device and other devices, your operating system, browser type and version, CPU speed, connection speed, and locale information based on IP address. To the extent that IP addresses or similar identifiers are considered personal information by local law, we also treat these identifiers as personal information. The Site collects usage information, such as the numbers and frequency of user visits to our website and its components, We use this information to give a personalized experience to our users and also improve our services.
G. We also collect information about your purchases and activities on the Service, which we may use to present you with offers that we believe may be of interest to you. As part of this use of information, we may provide non-personally identifying, aggregate information to our Participating Publishers and other third parties about how our users, collectively, use the Service.
1. Articles you’ve read– To understand your interests and showcase more relevant articles
2. Time spent on reading each magazine and article– To analyze the quality of content and provide appropriate feedback to publishers
3. Web and app pages you’ve visited– To track features used by you and recommend features that you’ve not used
H. We send push notifications to our apps after getting consent from our users. These push notifications inform users about the latest offers, new issues going live, personalized magazines and articles. The users can disable push notifications anytime.
COOKIE POLICY
Cookies are alphanumeric identifiers that we transfer to your computer or device to enable our systems to recognize your browser and tell us how and when pages in our website are visited and by how many people.
Most browsers have an option for turning off the cookie feature, which will prevent or limit your browser from accepting new cookies, as well as (depending on the sophistication of your browser software) allowing you to decide on acceptance of each new cookie in a variety of ways. You may wish to leave the cookies activated because cookies enable you to take advantage of some of the Site’s most essential features.
SHARING OF YOUR PERSONAL INFORMATION
Personal Information will only be shared by Company to provide or improve our products, services, to contact you about our services; and with our advertisers to contact you about their new products etc; it will not be shared with third parties for their marketing purposes.
Others: We may access, read, preserve, disclose, or release Personal Information when we believe in good faith that release is necessary to comply with law and enforce or apply our Terms of Use; or protect the rights, property, or safety of Company, our employees, our users, or others.
SECURITY OF YOUR PERSONAL INFORMATION
We allow you to limit access to your account via a password for your privacy and security. If you access your account via a third party site or service, you may have additional or different sign-on protections via that third party site or service. You are responsible for ensuring against unauthorized access to your account and Personal Information by selecting and protecting your password and/or other sign-on mechanism appropriately and limiting access to your computer and browser by signing off after you have finished accessing your account.
We use industry-standard Secure Socket Layer (SSL) software to encrypt your Personal Information during transmission. However, because no data transmission over the Internet is completely secure, and no system of physical or electronic security is impenetrable, Company cannot guarantee the security of Personal Information in its possession or the security of its servers or databases. Unauthorized entry or use, hardware or software failure, and other factors, may compromise the security of user information at any time.
In the unlikely event that Company believes that the security of your Personal Information in its possession or control may have been compromised, Company may seek to notify you. If notification is appropriate, Company may notify you by email, messaging to your device, or other means within 72 hours of data compromise.
PERSONAL INFORMATION YOU CAN ACCESS
Company allows you to access the following information about you for the purpose of viewing, and in certain situations, updating that information: email address, name, location and marketing preferences. This list may change as the Service changes. The information you can view, update, and delete may change as the Website changes. If you have any questions about viewing or updating information, we have on file about you, please contact us at privacy@tionet.in or at The Indian Optician., A-99 Defence colony, New Delhi – 110024
You can add or update certain personal information on your account, such as name and email address. When you update information, however, we often maintain a copy of the unrevised information in our records.
Upon your written request to privacy@ tionet.in we will remove your Personal Information from our active user database provided that (a) you are current with all payment obligations, (b) we do not believe it reasonably necessary to keep such information for any pending legal action, and (c) we are under no obligation to retain such information. Please be aware that any unfulfilled subscriptions may be cancelled without refund and you will have to re-register in order to use the Service. It is your responsibility to request a refund from us.
TRADEMARKS
All names, images, logos identifying The Indian Optician are proprietary marks of The Indian Optician. All third-party brand, product, service and company names contained on this Website are the trademarks, service marks and trade names of their respective holders. TIO do not give permission for their use by any person other than the holders. Any such use may constitute an infringement of the holders’ rights.
EXTERNAL LINKS
The Indian Optician do not represent, warrant, endorse or hold responsibility over any external sites that may be linked to and from this Website. Any external site that you visit by clicking through a link on this Website is outside the control of TIO and you visit entirely at your own risk.
These Terms and Conditions and the other rules, guidelines, licenses and disclaimers posted on the Service (on the tionet website or tionet Apps constitute the entire agreement between tionet and you with respect to your use of the Service and supersede all previous written or oral agreements between us with respect to the subject matter hereof.
From time to time, tionet may revise these Terms and Conditions to keep them up to date with tionet products and services. Please refer to the tionet website and tionet Apps periodically for any changes. The update date first written above is used to alert you to recent modifications. Your access or use of the Service subsequent to such an update will signify your assent to be bound by such changes.
If you have any questions regarding our terms and conditions, please email us at infotiodel@gmail.com
JURISDICTION
These Terms & Conditions shall be governed by and construed in accordance with the laws of India. Disputes arising here from shall be exclusively subject to the jurisdiction of the courts of New Delhi to the exclusion of any other. If any of these Terms should be determined to be illegal, invalid or otherwise unenforceable by reason of the laws; it shall be severed and deleted from this clause. All other Terms of Use and Terms & Conditions shall remain in full force and continue to be binding and enforceable. The Indian Optician reserves the right to change any of its terms and conditions at any time by posting changes online.
LEGAL DISCLAIMERS
By registering on tionet.com and agreeing to its Terms of Use and Privacy Policy, you also agree and acknowledge the following Legal Disclaimer notice:
a. You agree that the use of tionet.in, the application and its services, are at solely at your own risk. Neither tionet.in nor its associates nor employees nor third party content providers guarantee that the service will be completely uninterrupted or error-free or fool proof against miscreant activities. Nor do they warranty that you will get the exact results as expected or promised by the website or product.
b. The website and the application are provided on an “AS IS” basis with no warranties expressly stated or promised regarding the results that would be obtained from the use of it.
c. In no event will TIONET.IN or any person or entity or third party involved in the creation, production and distribution of the content on the website and the application be liable in contract or legally for any damages, including and not limited to, direct, indirect, incidental, special, and consequential incurred to you while or on using tionet.com. By registering on the website or downloading the application, you agree that the provisions mentioned in this section shall apply to all use of and content on the website and the application.
d. The above disclaimer of liability applies to any damages or injury caused by any failure of performance, error, omission, inaccuracy, interruption, deletion, delay, defect in operation or transmission, computer virus attack, communication line failure, theft or destruction or unauthorised access to, alteration of or use of this website, on account of breach of contract or negligence or under any other cause of action.
e. You specifically acknowledge that tionet.com is not liable for any kind of defamatory or offensive or illegal conduct of other users or third parties or their content and that the risk of injury from the foregoing rests entirely with you.